Fig. 4. Analysis of selected de novo designs.
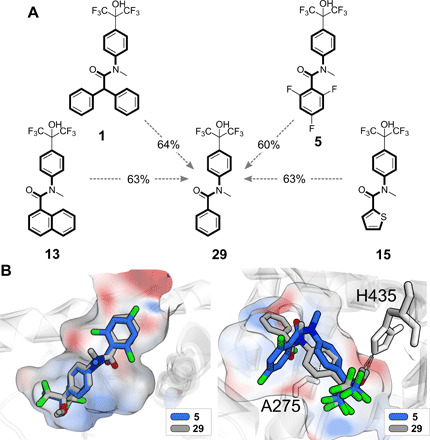
(A) Selected de novo designs (1, 5, 13, and 15; Table 1), with atomic scaffolds highlighted with a thicker line, in comparison with the most similar fine-tuning compound (29, ChEMBL-ID: 379225, LXRα: EC50 = 0.4 μM, LXRβ: EC50 = 0.18 μM). The corresponding fragment similarity (Morgan molecular fingerprints and Tanimoto index) is indicated in percentage values. Compounds 1, 13, and 15 have novel atomic scaffolds compared to the known LXR modulators annotated in the ChEMBL27 database. Compound 5 has a similar agonistic effect on LXRα to compound 29, and it is five times more selective for the α subtype. (B) Automated ligand docking of compounds 5 (de novo design, blue) and 29 (fine-tuning compound, light gray) to the binding pockets of LXRα [PDB ID: 3IPS (63), left] and LXRβ [PDB ID: 1PQC (64), right]. GOLD (65) docking software was used. The solvent-accessible surface of the binding pockets is colored according to the computed electrostatic potential; red: negatively charged and blue: positively charged.
