Fig. 4. Examination of sperm damage after fertilization.
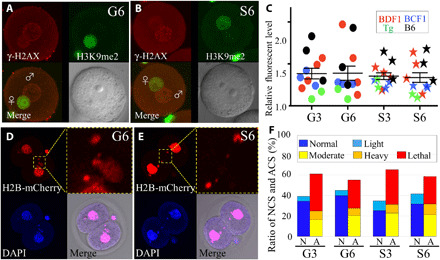
(A and B) Immunostaining of zygotes derived from G6 ground control (A) or S6 space sperm (B) by the anti–γ-H2AX antibodies. The foci of γ-H2AX signals show DNA double-strand breaks (top left, red). Female pronuclei were detected by H3K9me2 immunostaining (top right, green). Merged images (bottom left) and light microscopy image (bottom right). (C) The brightness of each male pronucleus was plotted. Nuclear staining of two-cell embryos derived from G6 ground control (D) and S6 space sperm (E). ACS was detected by H2B-mCherry mRNA injection (top left and its high magnification, red) and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; bottom left: blue) at the two-cell stage. The double-positive parts were judged as micronuclei using merged images (bottom right). (F) The ratio of normal chromosome segregation (NCS) and ACS. N, NCS; A, ACS. Light blue shows the rate of light ACS, but it was included in NCS. Photo credits: (A and B) Sayaka Wakayama and (D and E) Masatoshi Ooga, University of Yamanashi.
