Figure 1.
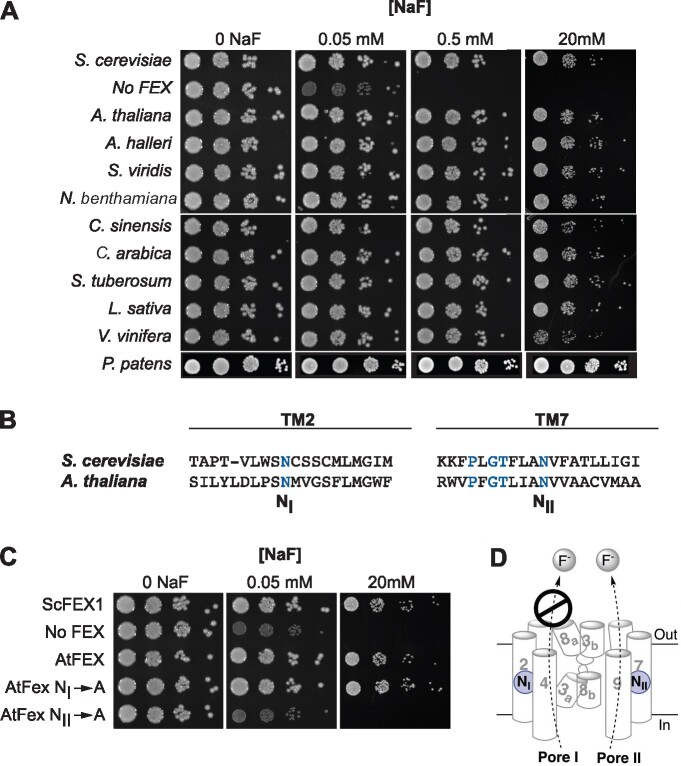
Any plant FEX rescues the yeast FEX DKO. A, DKO yeast were transformed with cDNA sequences of FEX homologs from the indicated plants and 10-fold dilutions of yeast cultures at OD600 of 1 were tested on plates with increasing amounts of NaF. B, Relative positions of the conserved N in yeast and A. thaliana sequences. Blue lettering highlights conserved amino acid residues. C, Growth assay of yeast DKO transformed with N to A substitutions. Rescue of yeast DKO fails only when A is substituted for N in TM7/Pore II. D, Model of FEX in cellular membrane based on bacterial crystal structure and yeast modeling. Cylinders and numbers denote transmembrane domains. A conserved N (blue circle) is positioned in both Pore I and II. In yeast, Pore II is a functional conduit for fluoride ions and Pore I is not.