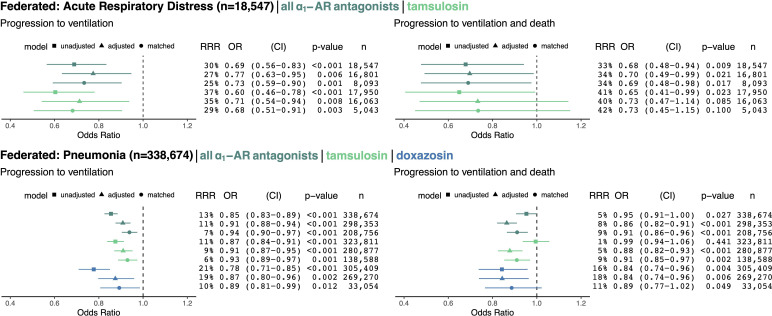
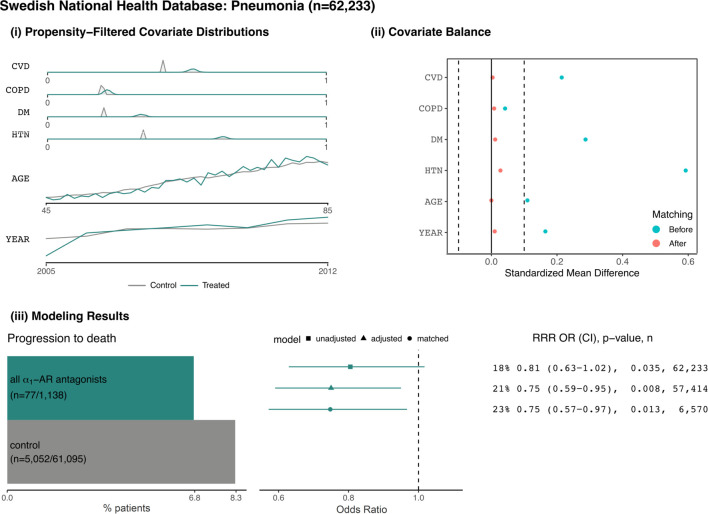
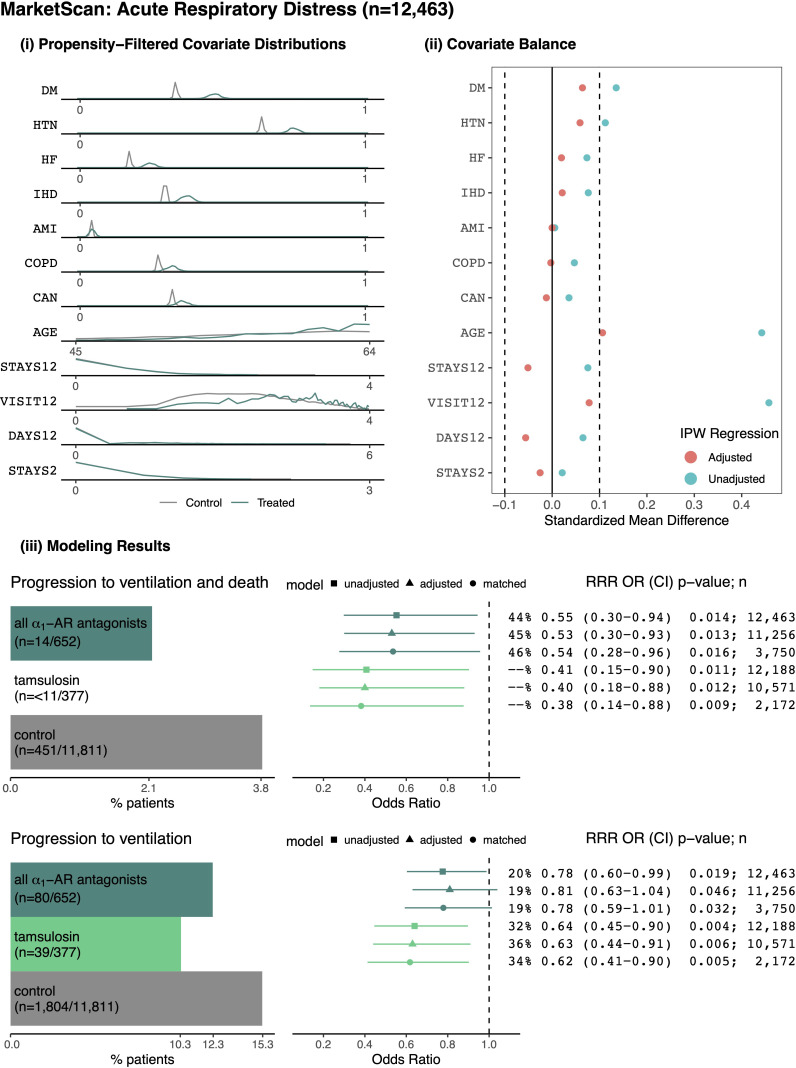
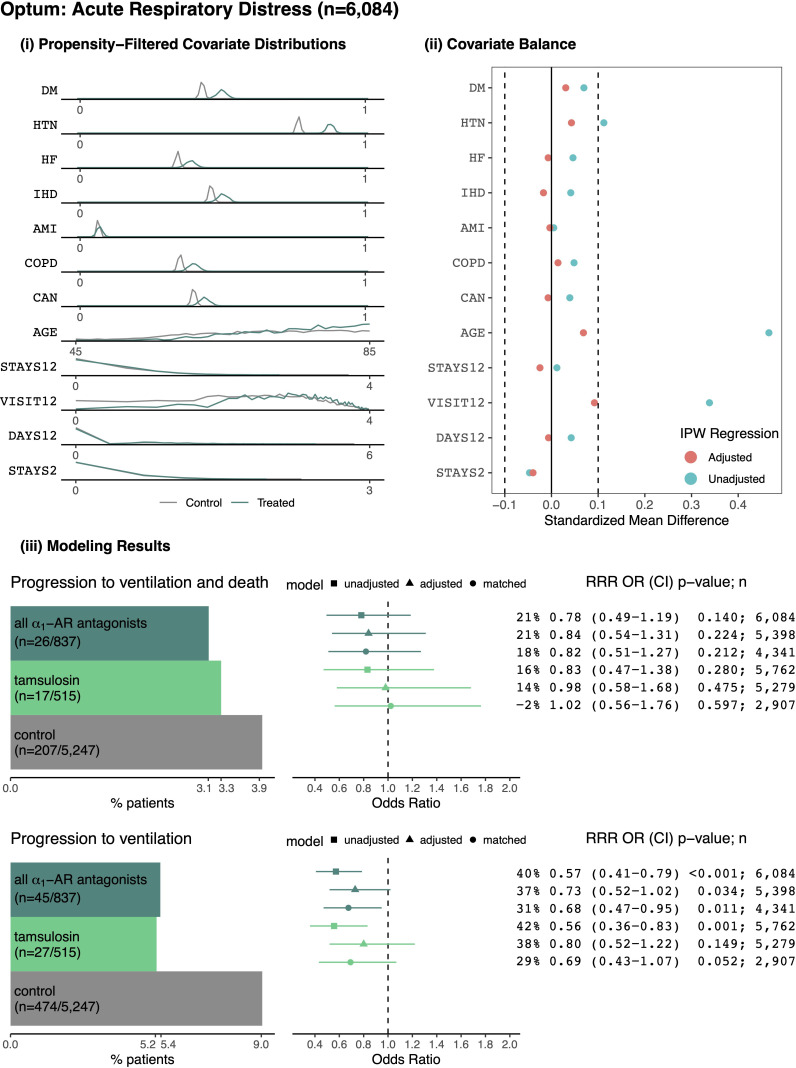
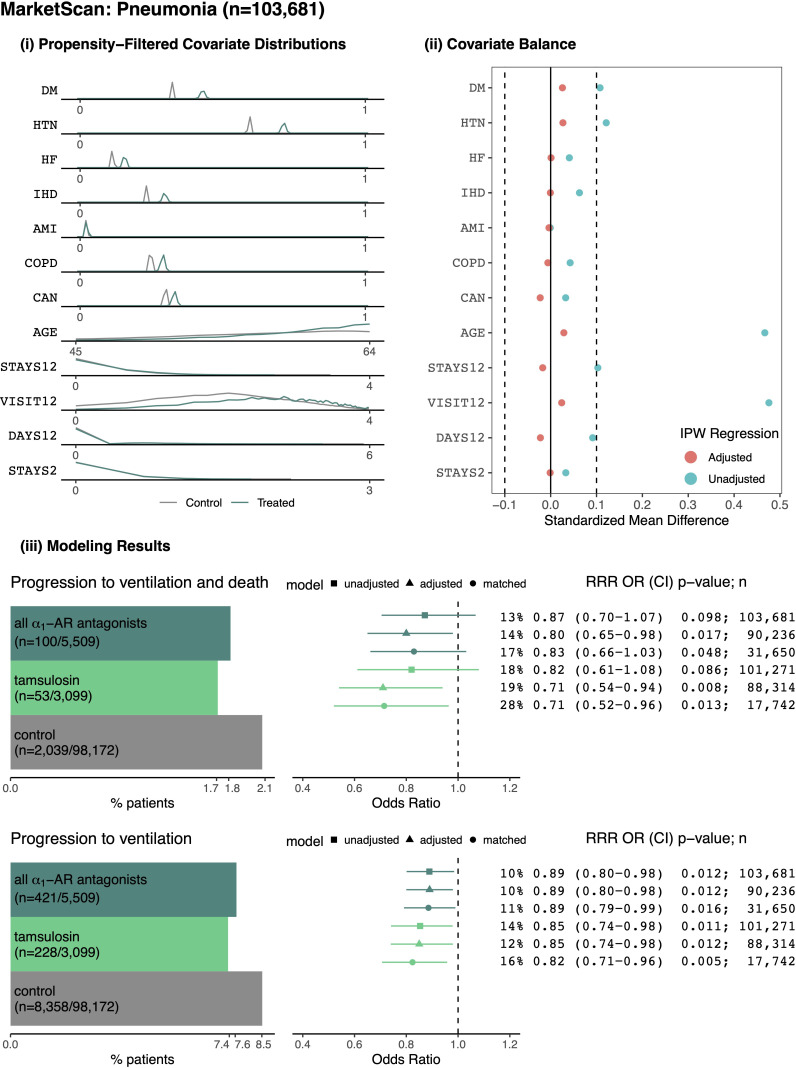
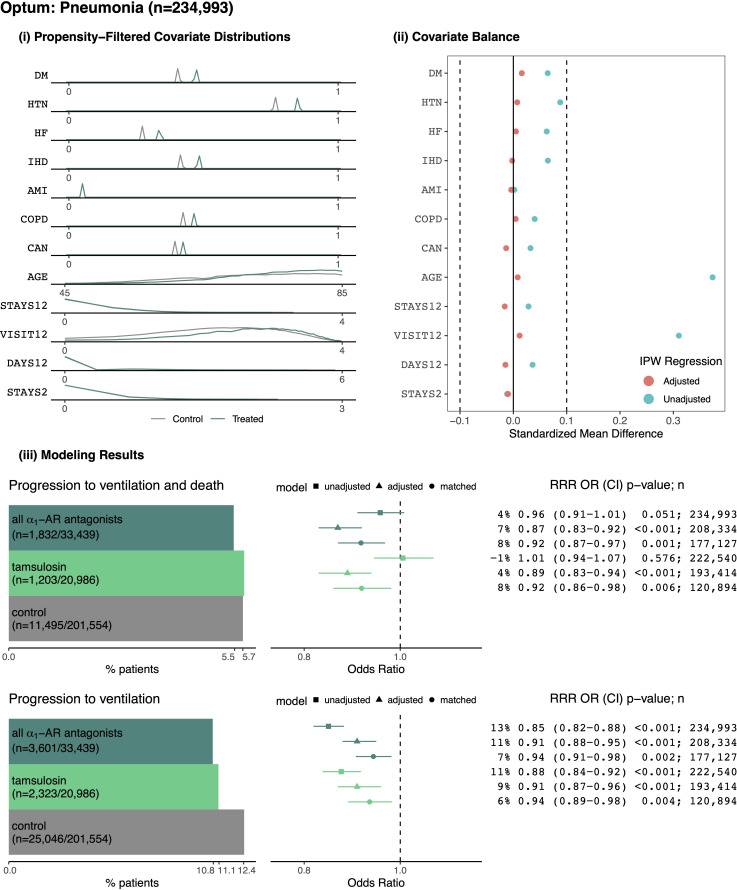
Figure 3. Cohorts across datasets (MarketScan and Optum) associated with the same disease (ARD in top row, pneumonia in bottom row) were pooled using federated causal learning techniques described in Materials and methods.
In each quadrant, we show: (left) plotted odds ratios (OR) with confidence intervals (CI), and (right) values for relative risk reductions (RRR), OR, CI, p-values (p), and sample sizes (n) for unadjusted, adjusted, and matched models, including any ⍺1-AR antagonists or specifically tamsulosin or doxazosin. We only study exposure to doxazosin in the pneumonia cohorts since there is insufficient statistical power to analyze the drug in ARD cohorts. Results are shown for outcomes of mechanical ventilation (left column) and mechanical ventilation leading to death (right column). In general, ⍺1-AR antagonists were associated with reducing risk of adverse events across exposures, outcomes, and modeling approaches. Each federated analysis yielded an OR point estimate below 1.