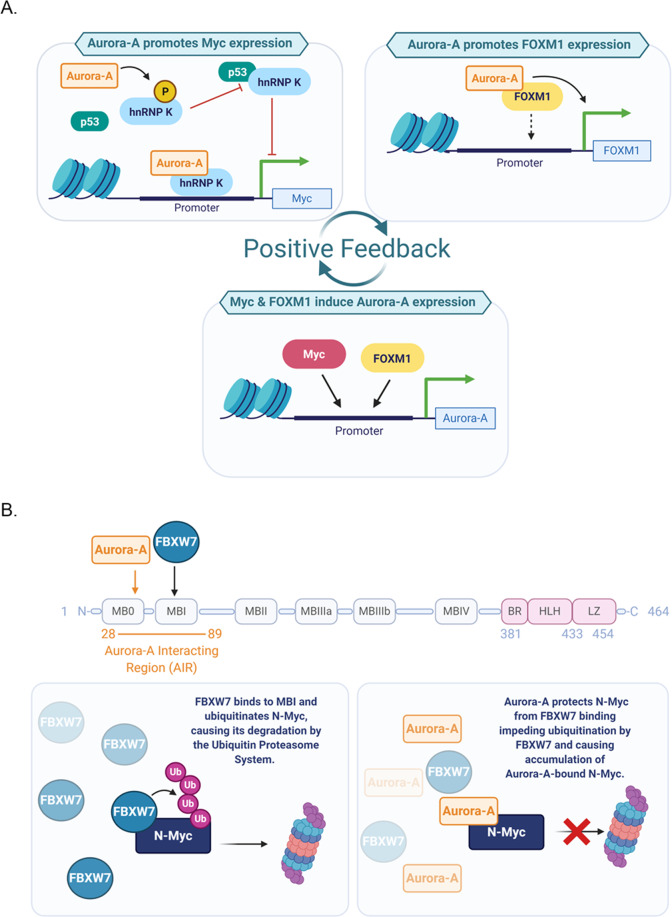
Fig. 2. Aurora-A functions in regulating transcription and stability of oncoproteins.
A Aurora-A can increase Myc expression directly, through promoter shift, in combination with hnRNP K; a potential indirect effect, also mediated by hnRNP K, may also represent an indirect Aurora-A contribution to elevated Myc levels. The right panel schematises the transcriptional effect of Aurora-A on FOXM1 gene expression. The dashed arrow indicates potential direct binding of an Aurora-A/FOXM1 complex to the FOXM1 promoter. In turn, Myc and FOXM1 can upregulate AURKA gene expression. B The N-Myc protein sequence is schematically represented on top; myc boxes and DNA-binding domains are indicated, as well as the binding regions to Aurora-A and FBXW7. FBXW7 recognises and ubiquitinates N-Myc, inducing proteasome-mediated degradation (lower left panel). Aurora-A binding protects N-Myc from FBXW7-mediated degradation (lower right panel). Created with BioRender.com.