Figure 1:
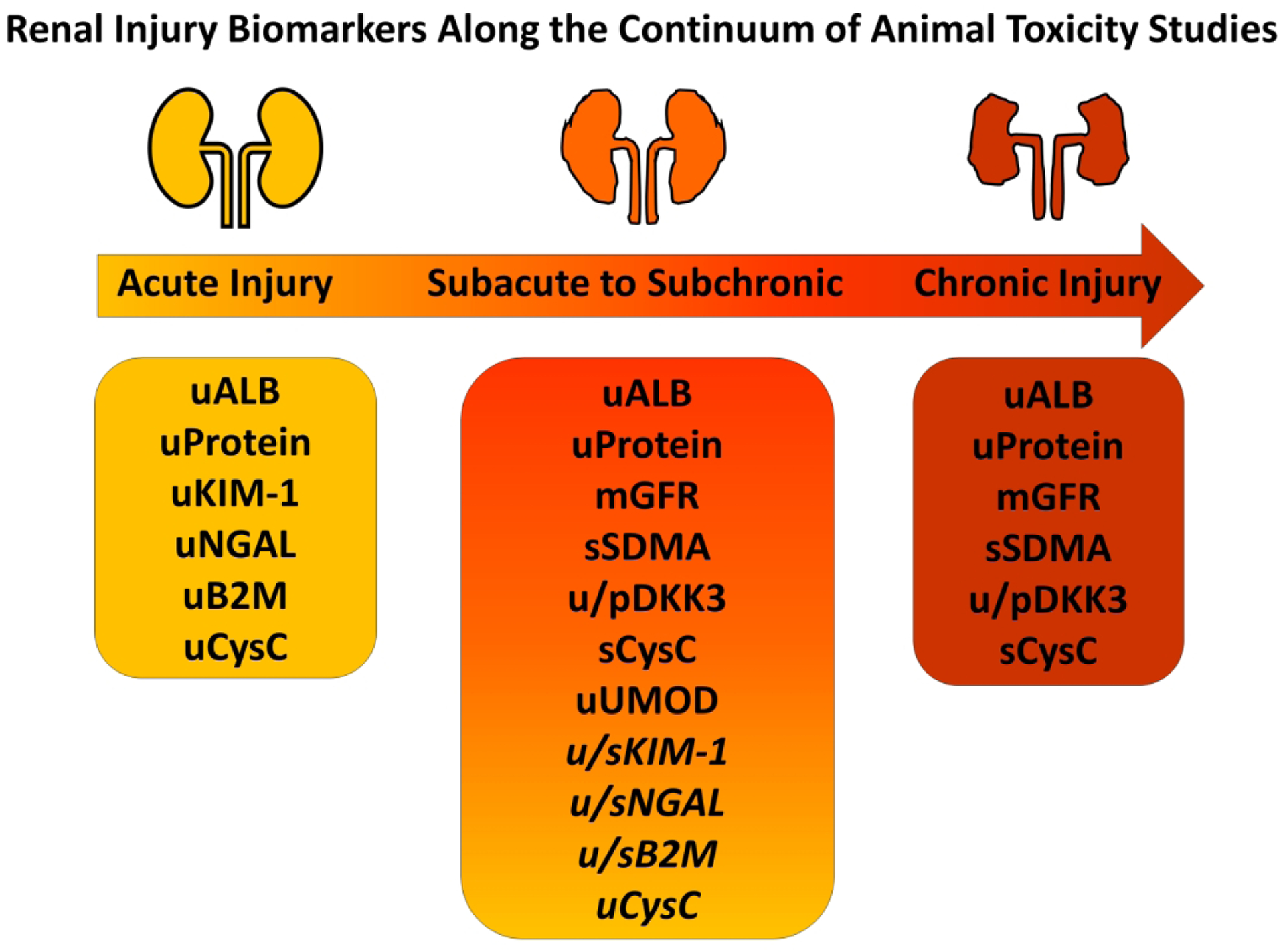
Renal Injury Biomarkers Along the Continuum of Animal Toxicity Studies. Acute renal injury biomarkers (KIM-1, NGAL, B2M, urine CysC) have shown some utility in monitoring the progression of acute to chronic injury, but often their successful usage in subacute to subchronic renal injury has been dependent upon type of injury and/or species (italicized). In addition to the standard renal functional biomarkers (ALB, Protein, mGFR), other biomarkers have shown promise in predicting and monitoring subacute to subchronic (SMDA, DKK3, serum CysC, UMOD) or chronic renal injury (SDMA, DKK3, serum CysC) in animal toxicity studies. u: urine, s: serum, p: plasma, kidney injury molecule 1: KIM-1, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: NGAL, beta 2 macroglobulin: B2M, cystatin C: CysC, symmetrical dimethyl arginine: SDMA, dickkopf homolog 3: DKK3, uromodulin: UMOD, albumin: ALB, measured glomerular filtration rate: mGFR.
