Figure 3: A summary of alterations in MAMs for two neurodegenerative diseases: PD and AD.
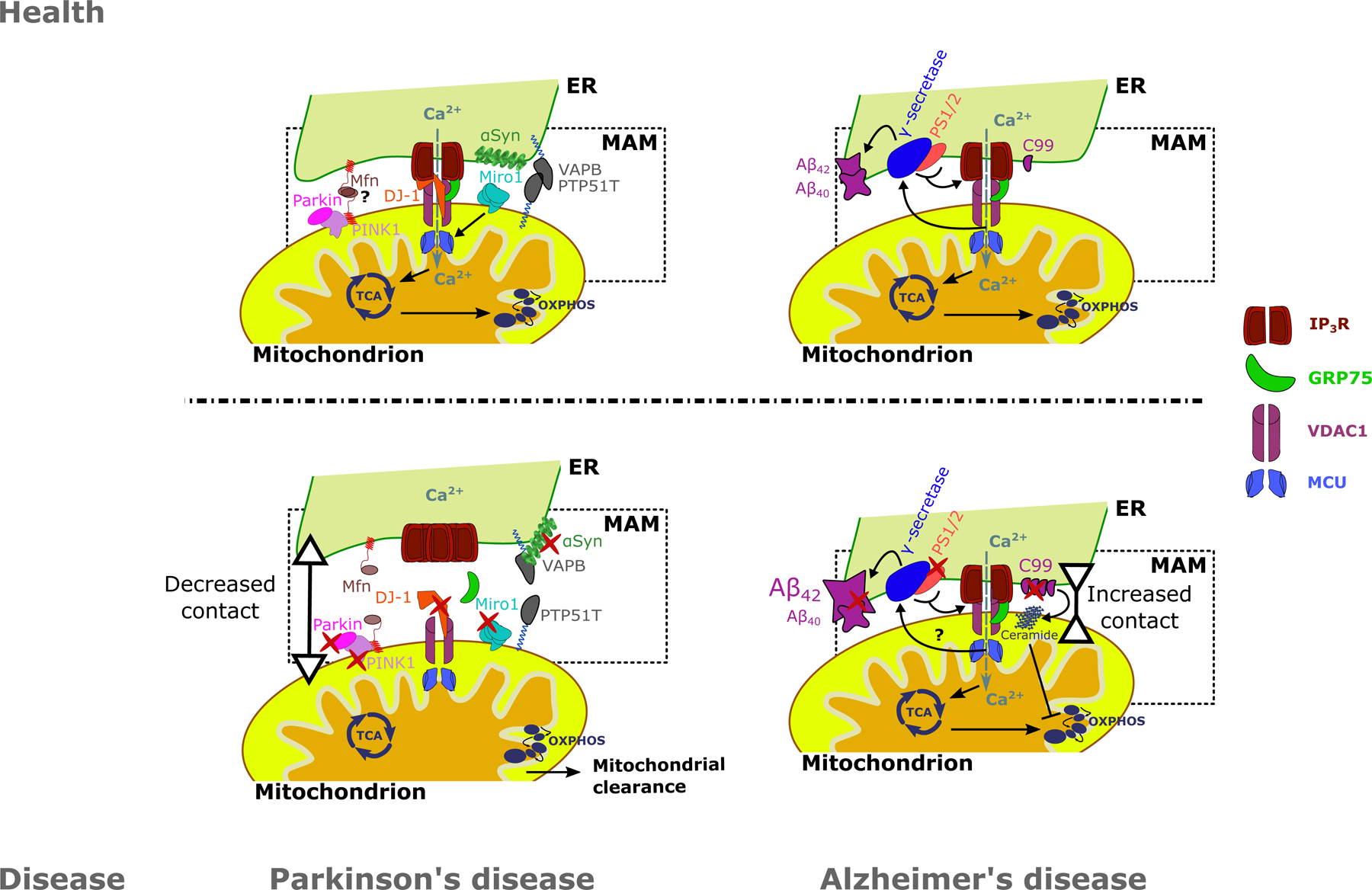
A: DJ-1, a protein associated with familial forms of PD, is a vital component of the IP3R-VDAC1-GRP75 axis in the MAMs. Loss of function of DJ-1 results in decreased ER-mitochondrial Ca2+ transfer, ER-mitochondrial contact sites and upregulation and aggregation of IP3R. PD-related proteins PINK1 and Parkin have been implicated in the tethering of ER to mitochondria. Moreover, Miro1 positively regulates mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake by MCU and mutations in Miro1 result in decreased ER-mitochondrial contact. Additionally, αSyn, of which its aggregated form is a hallmark of PD, is also present in the MAMs. Both WT and mutant αSyn interact with the VAPB-PTPIP51 MAM tethering proteins. B: AD is characterized by the deposition of Aβ plaques due to aberrant APP processing. Processing of APP is performed by the γ-secretase complex, of which PS1 and PS2 are components. APP and PS1–2 are particularly enriched in the MAMs. Mutations in APP, PS1–2 can increase ER-mitochondrial contact. Additionally, mutant PS1–2 are able to sensitize IP3Rs to IP3, increasing ER-mitochondrial Ca2+ transfer, which in turn enhances APP processing. C99, a product of APP processing, is enriched in the MAMs in AD patients cells, where they enhance the accumulation of ceramide in the mitochondria. In turn, ceramides inhibit mitochondrial respiration. Ultimately these changes lead to an increased Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio in AD patient cells. Red marks indicate alterations on the protein level in neurodegeneration, leading to decreased ER-mitochondrial contact in PD and increased ER-mitochondrial contact in AD. Grey arrows indicate Ca2+ fluxes. Question marks signify processes that are still uncertain. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum, MAM: Mitochondria-associated ER membrane, TCA: Tricarboxylic acid cycle, OXPHOS: oxidative phosphorylation, Ca2+: Calcium ion, IP3R: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 1, GRP75: Glucose-regulated protein 75, VDAC1: Voltage dependent anion channel 1, MCU: Mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter, Mfn: Mitofusins, PINK1: PTEN-induced kinase 1, DJ-1: Protein deglycase DJ-1, Miro1: Mitochondrial Rho GTPase 1, VAPB: Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C, PTPIP51: Protein tyrosine phosphatase interacting protein 51, αSyn: α-synuclein, Aβ42/40: 42/40 amino acid proteolytic product of amyloid precursor protein, PS1/2: Presenilin 1 / 2, C99: C99 fragment of amyloid precursor protein.
