Figure 1.
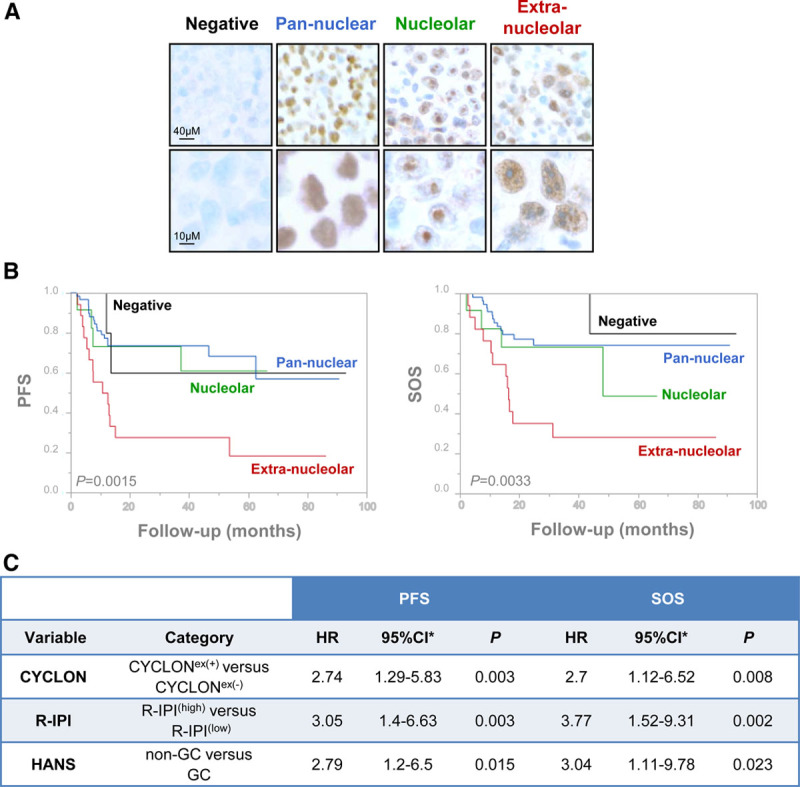
CYCLON subcellular localization define prognosis subgroups in DLBCL patients. (A), IHC analysis of CYCLON revealing distinct expression patterns in DLBCL patients as indicated. (B), Kaplan-Meier analyses of PFS (left) and SOS (right) associated to CYCLON patterns. P values are derived from a log-rank test. PFS, extranucleolar: 18.52% (95% CI, 3.98–41.4); nucleolar: 61.11% (95% CI, 25.46–83.75); diffuse: 56.91% (95% CI, 30.7–76.4); negative: 60% (95% CI, 12.57–88.18); SOS: extranucleolar: 31.11% (95% CI, 11.36–53.43); nucleolar: 48.89% (95% CI, 8.8–81); diffuse: 74.85% (95% CI, 60–84.75); negative: 80% (95% CI, 20.38–96.92). (C), Multivariate bootstrap Cox regression analyses of CYCLON extranucleolar staining status (+/−), R-IPI (high/low), and Hans’ classification (GC/non-GC) for PFS and SOS. *Normal-approximation 95% CI based on bootstrap resampling (1000 replicates). Schoenfeld residual test, PFS model: global P = 0.58 and SOS model: global P = 0.72; Harrell’s C statistic, PFS model: C = 0.72 and SOS model: C = 0.77. CI = confidence interval; DLBCL = diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; GC = germinal center; Hans = Hans algorithm defining non-GC and GC DLBCL subtypes; HR = hazard ratio; IHC = immunohistochemical; PFS = progression-free survival; R-IPI = revised version of the International Prognostic Index; SOS = specific overall survival.
