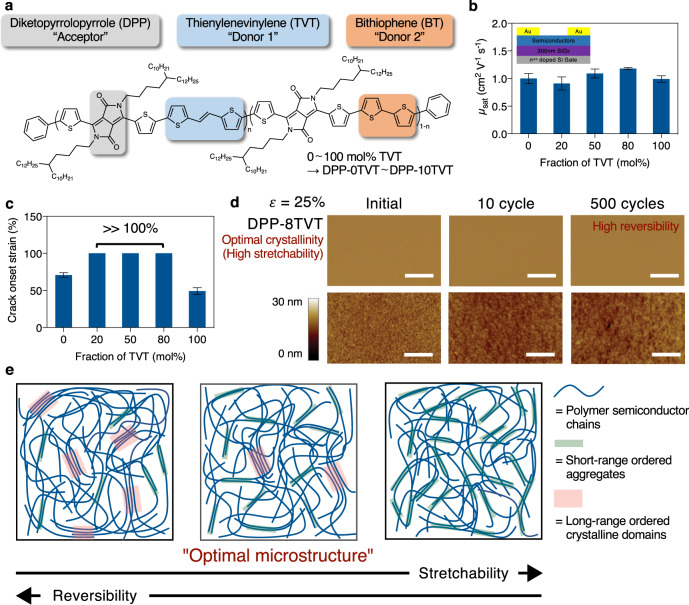
Fig. 1. Molecular design and properties of stretchable terpolymers.
a Chemical structure of terpolymers used in this study. Based on the TVT unit fraction, terpolymers were named as DPP-0TVT (0 mol% TVT) ~ DPP-10TVT (100 mol% TVT). b Mobility of the terpolymers measured from top-contact-bottom-gate transistors given in the top left corner (measured in air). Error bars represent SD. c Crack onset strain of the terpolymers. Our terpolymers showed tremendous crack onset strain >100% strain. Error bars represent SD. d Optical and AFM images of 30 nm-thick semiconducting terpolymer films after repeated 25% strain. DPP-8TVT showed high mechanical reversibility without wrinkling. The color scale of the AFM images represents relative height (scale bar: 10 µm and 1 µm for optical and AFM images, respectively). e Microstructures of polymer semiconductors that are ideal for stretchability and mechanical reversibility. Semi-crystalline polymer semiconductors with low crystallinity (such as DPP-8TVT) have optimal microstructures with balanced stretchability and mechanical reversibility.