Figure 4.
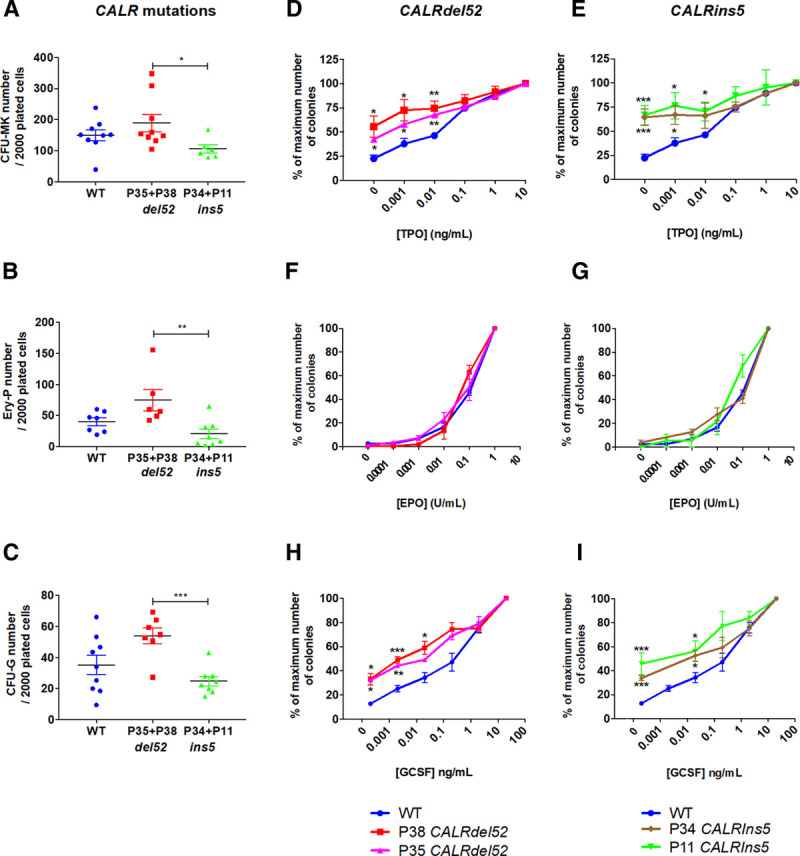
CALRdel52/ins5 increase sensitivity to TPO and G-CSF. (A), Cloning efficiency of CD34+CD43+ progenitors in the presence of SCF and TPO. (B), Cloning efficiency of CD34−CD43+ progenitors in the presence of SCF and EPO. (C), Cloning efficiency of CD41−CD34+CD43+ progenitors in the presence of SCF and G-CSF. (D, E), Sensitivity of CFU-MK to TPO (mean ± SEM, WT: n = 7; P38: n = 6, P35: n = 3, P11: n = 3, P34: n = 3). (F, G), Sensitivity of EryP to EPO (mean ± SEM, WT: n = 7; P38: n = 4, P35: n = 3, P11: n = 3, P34: n = 4). (H, I), Sensitivity of CFU-G to G-CSF (mean ± SEM, WT: n = 6; P38: n = 4, P35: n = 3, P11: n = 3, P34: n = 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Student t test. CFU-G = colony forming unit-granulocyte; CFU-MK = colony forming unit-megakaryocyte; EPO = erythropoietin; EryP = erythroid progenitor; G-CSF = granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; SCF = stem cell factor; SEM = standard error of the mean; TPO = thrombopoietin; WT = wild-type.
