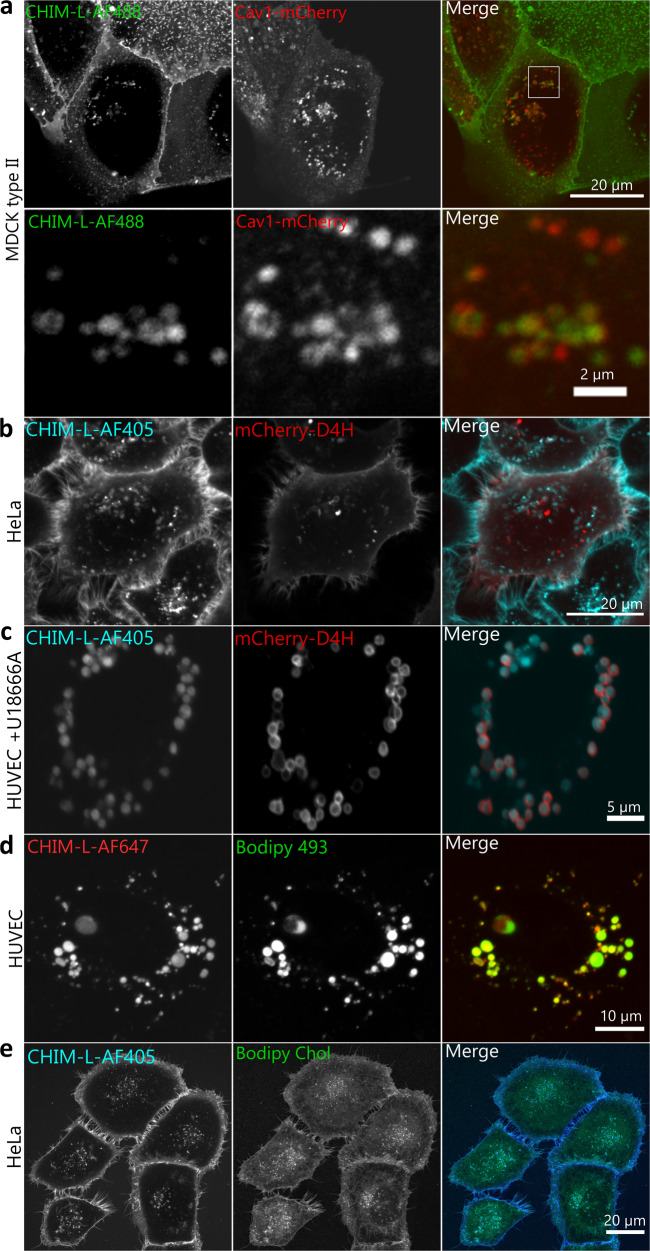
Fig 4. CHIM-L mimics the cholesterol distribution in live cells.
Stills of live cell microscopy recordings revealing the CHIM-L distribution in epithelial cell lines and primary endothelial cells in comparison to different markers. a Caveolin1 (mCherry) enriched structures partially colocalize with fluorescently labeled CHIM-L (AF488) in MDCK cells. The inset of the merged panel is shown at higher maginfication in the bottom row. b CHIM-L (AF405) colocalizes with the ectopically expressed cholesterol-binding probe mCherry-D4H at the plasma membrane and some membrane invaginations/internal structures in HeLa cells. c Treatment with the NPC1 inhibitor U18666A, which results in cholesterol accumulation in enlarged late endosomes, sequesters CHIM-L (AF405) into these late endosomes that are also stained with mCherry-D4H in primary endothelial cells (HUVEC). d Lipid droplets stained with Bodipy 493 in comparison to CHIM-L (AF647) in HUVEC. e HeLa cells co-incubated with CHIM-L (AF405) and BODIPY-cholesterol as described in Materials and Methods. Note that CHIM-L shows a more profound plasma membrane staining.