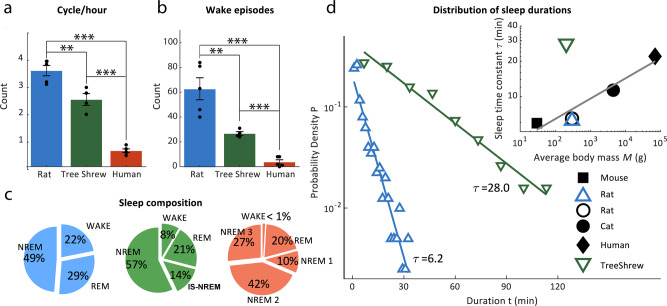
Fig. 4. Tree shrews have significantly longer and less fragmented sleep than rats.
a Bar chart is showing average count of sleep cycles per hour across species, Rats n = 5, tree shrews n = 4, humans n = 5. Note, significantly more sleep cycles per hour in rats in comparison to tree shrews. b Bar plot is illustrating the mean count of wake bouts over the course of the recording period across species. Rats have significantly more wake episodes than tree shrews. c Pie charts showing the mean fractions of different behavioral stages after sleep onset in tree shrews, rats, and humans respectively. d Distributions of sleep bout durations for rats and tree shews. The data of both species follows a power law function with different time constants, τ. Lines between data points indicate the fit of the function for tree shrew and rat in green and blue respectively. The inset shows values of the time constant τ for the distribution of sleep duration in relation to the body mass of different species. Human, mouse, rat, and cat data, black markers were taken from a previous publication34. Note that values obtained here for the rat match those of the previous study. Tree shrew and rat τ values are added based on our own data and analyses. Error bars reflect the standard error of the mean.