Figure 3.
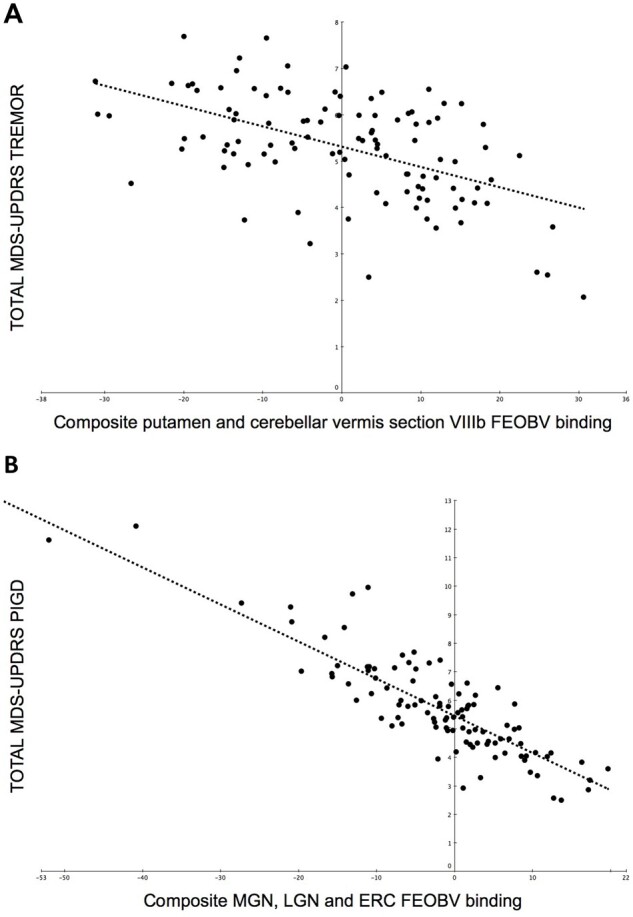
Scatter plots of topographic FEOBV binding and clinical ratings for tremor scores (A and PIGD ratings (B). Motor ratings were adjusted for covariates of age of onset, duration of motor disease and levodopa equivalent dose. For the PIGD plot composite medial geniculate nucleus (MGN), lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and entorhinal cortex (ERC) FEOBV binding were used. The composite FEOBV binding was computed as the average percentage of mean binding (derived from the complete volumes of interest) in normal control persons for the three volumes of interest. Although the covariates may be driving some of the regressor effects the FEOBV binding achieved significance independent of the covariates (F = 28.16, P < 0.0001). For the tremor plot composite putamen and cerebellar vermis section of lobule FEOBV binding was also computed as the average percentage of mean binding in normal control persons and also achieved significance independent of the covariates (F = 4.51, P = 0.036).
