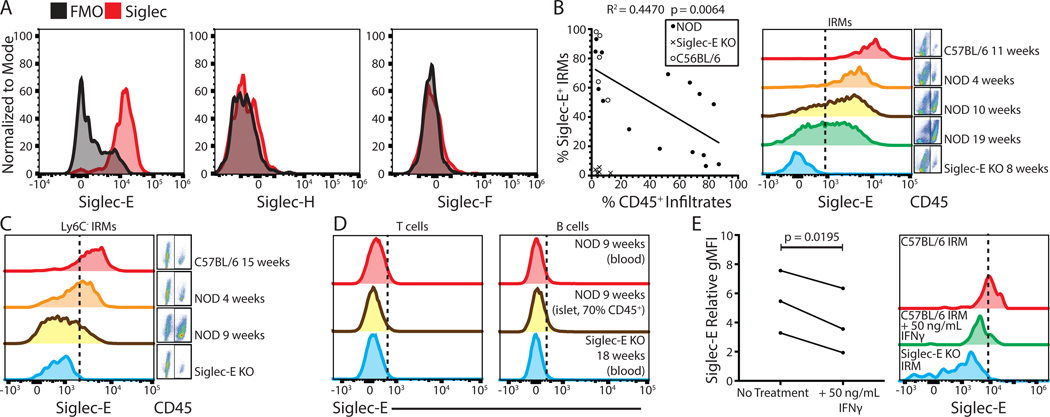
Figure 1. Islet resident macrophages express Siglec-E and cell surface expression is reduced with inflammation.
(A) Examination of Siglec E, H, and F expression on IRMs (defined as live, single CD45+ CD11c+ F4/80+ CD103− cells) compared to fluorescence minus one controls. (B) Correlation of CD45+ infiltrates (insulitis) vs. Siglec-E expression on IRMs in C57BL6/J (n = 5), NOD (n = 15), and Siglec-E KO control mice (n = 5). Linear regression analysis was performed for NOD data points. (C) Siglec-E expression on Ly6C- IRMs. (D) Siglec-E expression analysis on T or B cells (defined as live, single, TCRβ+ or CD19+ cells, respectively). (E) Siglec-E expression on IRMs after 24-hour C57BL/6J islet culture with 50 ng/mL IFNγ (n = 3). A paired T test was performed. All histograms are representative of at least three independent experiments with at least three mice in total.