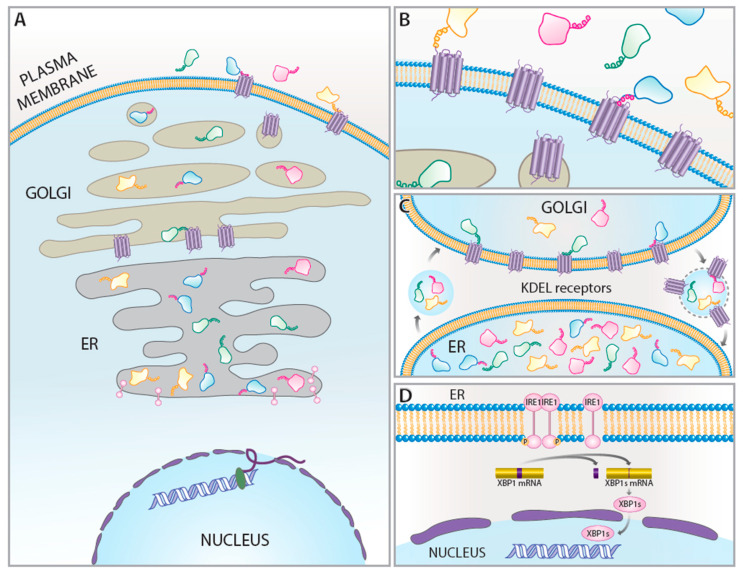
Figure 1.
(A) When proteins with ER retention sequences move along the secretory pathway they encounter KDEL receptors in the cis-Golgi. KDEL rectors recognize the carboxy terminus ER retention sequence of these proteins and traffic the proteins back to the ER lumen. (B) KDEL receptors in the plasma membrane modulate cell surface binding of ERS-containing proteins. Following ER stress, there is an increase in KDEL receptors found at the cell surface. (C) ERS-containing proteins that escape from the ER interact with KDEL receptors in the Golgi. The KDEL receptor-protein complex moves from the Golgi to the ER through COPI-mediated retrograde transport and the ER protein is release into the ER lumen. (D) ER stress leads to dissociation of BiP and IRE1α complexes, allowing for IRE1α oligomerization. Auto-phosphorylation of oligomerized IRE1α activates its kinase and RNase activities to initiate XBP1 splicing. Spliced XBP1 translocates to the nucleus to induce transcription of UPR genes, like the KDEL receptors.