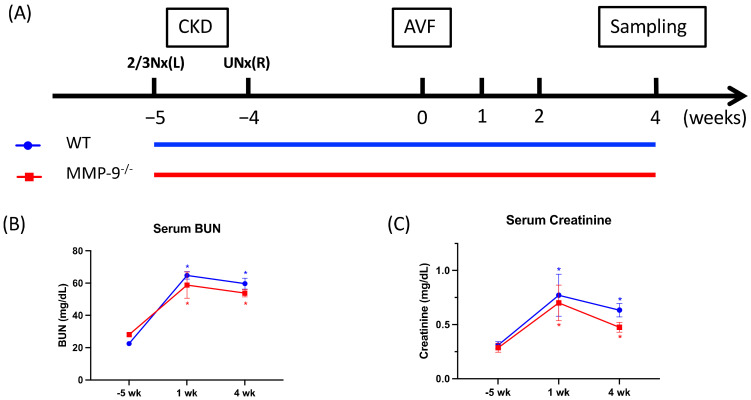
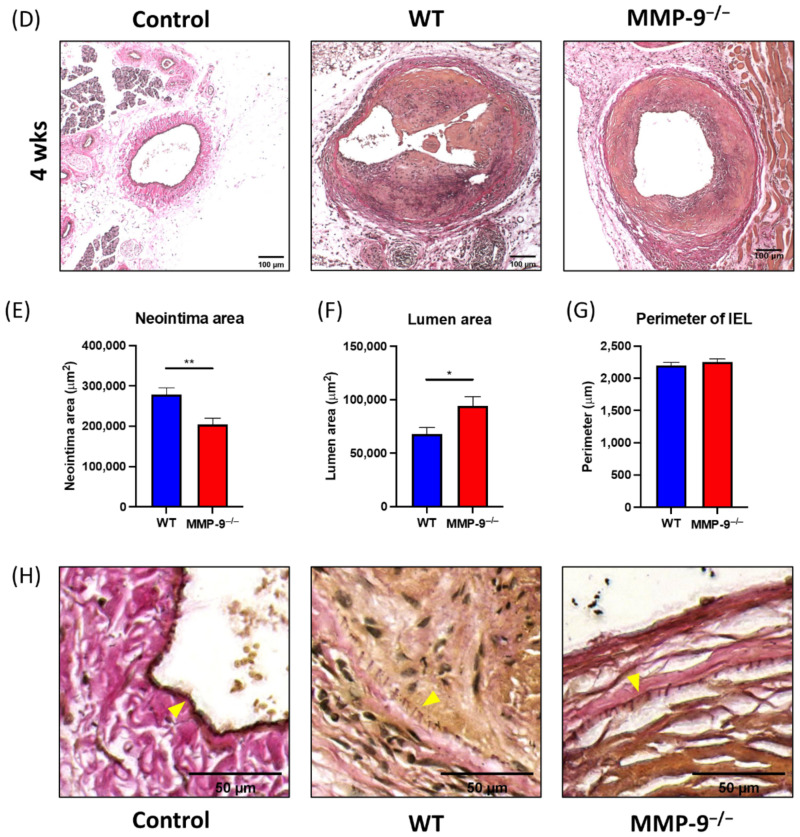
Figure 3.
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) knockout attenuated neointima formation and increased lumen size in arteriovenous (AV) fistula venous segment. (A) AV fistula was created in both wild-type (WT) and MMP-9−/− mice to examine the influence on AV fistula. (B,C) Chronic kidney disease was successfully induced in both WT and MMP-9−/− mice with significantly elevated serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine. (D) Morphometric analysis was done after elastin staining, scale bar = 100 μm. (E) Neointima size decreased and (F) lumen area enlarged after MMP-9 knockout (p = 0.0013 and 0.0116, respectively). (G) Internal elastic lamina (IEL) perimeter was not significantly different between WT and MMP-9−/− mice. (H) IEL structure was examined under high magnification, and loose structure was found in both WT and MMP-9−/− mice AV fistula venous segment, scale bar = 50 μm. No visible detrimental effect was detected after MMP-9 knockout. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. Data presented as mean ± SEM. Data analyzed by Student’s t-test one-way, n = 6–7 in each group.