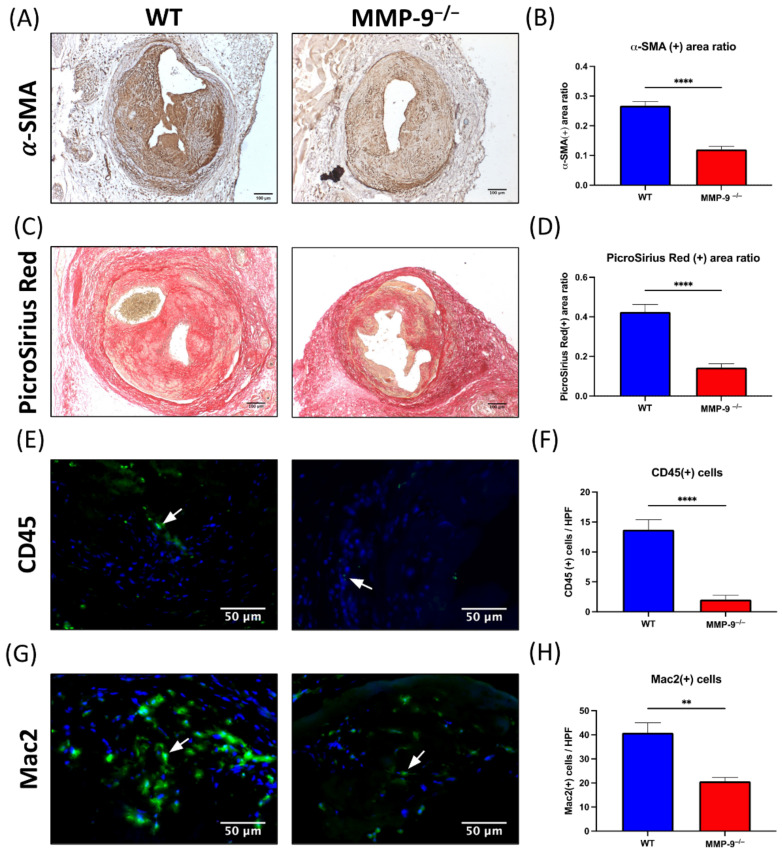
Figure 4.
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) knockout reduced α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) antibody and Picro Sirius stained area, and CD45(+) and Mac2(+) cells in neointima of AV fistula venous segment. (A) α-SMA(+) cells were the major cellular component within neointima. (B) The α-SMA(+) area ratio in neointima reduced after MMP-9 knockout (p < 0.0001). (C) Extracellular component of neointima was assessed with Picro Sirius Red staining. (D) The Picro Sirius Red(+) area ratio within neointima decreased in MMP-9−/− mice (p < 0.0001). (E) Leukocyte infiltration within neointima was determined by CD45 immunofluorescence. (F) MMP-9 deletion decreased CD45(+) cells/HPF in neointima (p < 0.0001). (G) Macrophages in the neointima was examined by Mac2 immunofluorescence. (H) The number of Mac2(+) cells/HPF decreased in MMP-9−/− mice (p = 0.0011). White arrows indicated positively stained cells. ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001. Data presented as mean ± SEM. Data analyzed by Student’s t-test one-way, n = 6–7 in each group. HPF, high power field.