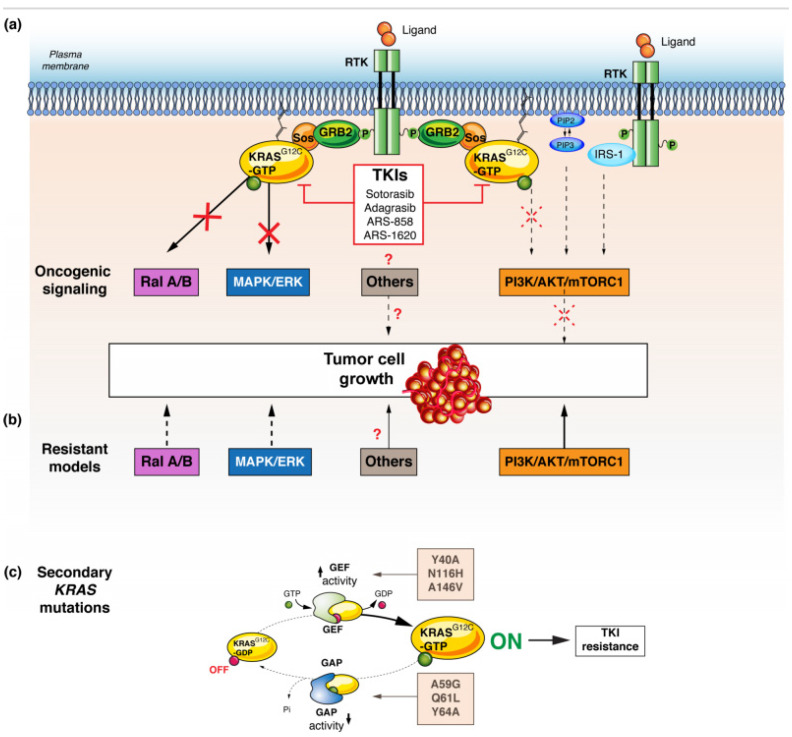
Figure 2.
Resistance mechanisms to KRAS G12C inhibitors. (a) KRAS G12C inhibitors preferentially block Ral A/B and MAPK pathways. (b) Resistance can occur when mutant KRAS signaling is predominantly through the PI3K or other parallel pathways. (c) Secondary KRAS mutations confer intrinsic resistance to targeted therapy by either potentiating nucleotide exchange (secondary mutations: Y40A, N116H, or A146V) or impairing inherent GTPase activity (secondary mutations: A59G, Q61L, or Y64A). Abbreviations: RTK: receptor tyrosine-kinase, KRAS: Kirsten rat sarcoma, GAP: GTPase activating proteins, GEF: guanine nucleotide exchange factors, SOS: son of sevenless, SHP2: Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-2, Ral: Ras-like, NF-kB: nuclear factor-kB, RAF: RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase, MEK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinase.