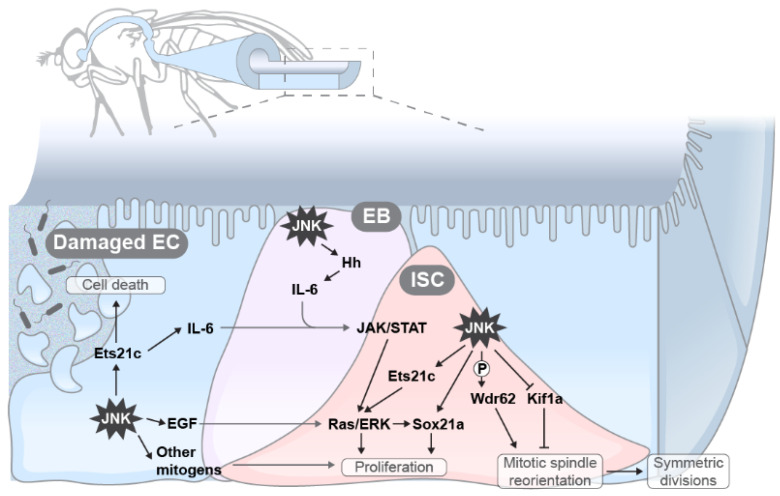
Figure 3.
The JNK pathway during homeostasis of the Drosophila gut. Damage or bacterial infection in the Drosophila midgut causes JNK activation in enterocytes (ECs). JNK induces expression of Ets21c, which then induces the secretion of inflammatory cues and mitogens such as IL-6 and EGFs. In cases of severe or chronic damage, JNK/Ets21c activity also induces apoptosis of the EC. Enteroblasts (EBs) activate JNK upon stress. This leads to the production of Hh, which acts in an autocrine manner to induce IL-6 production in EBs. In intestinal stem cells (ISCs), IL-6 and EGFs are received and integrated by the JAK/STAT and Ras/ERK pathways, respectively, to induce stem cell proliferation. Autonomous JNK pathway activation in ISCs upregulates its effectors Ets21c and Sox21a, which promote proliferation. In addition, JNK signaling induces symmetric divisions in ISCs by reorientating the mitotic spindle through its effector Wdr62 and by transcriptionally inhibiting Kif1a.