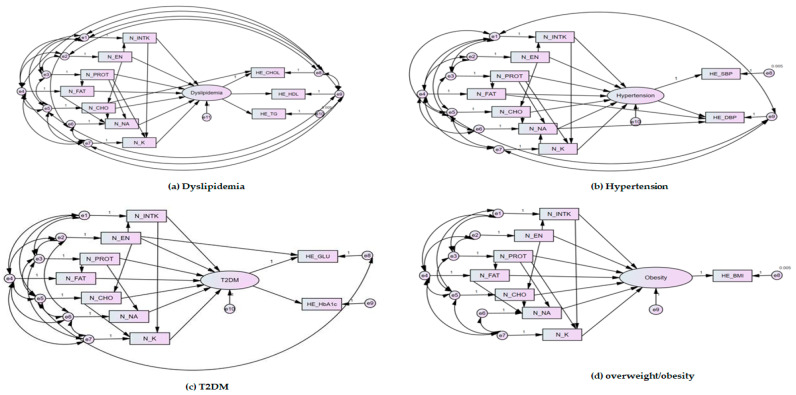
Figure 5.
Path diagrams for structural equation models: (a) dyslipidemia to nutritional intake; (b) hypertension to nutritional intake; (c) T2DM to nutritional intake; (d) overweigh/obesity to nutritional intake. N_CHO, carbohydrate intake (g); N_EN, energy intake (kcal); N_FAT, fat intake (g); N_INTK, food intake (g); N_K, potassium intake (mg); N_NA, sodium intake (mg); N_PROT, protein intake (g); HE_BMI, overweight/obesity; HE_chol, total cholesterol; HE_dbp, diastolic blood pressure (mean value of 2–3 blood pressure measurements); HE_glu, fasting blood glucose; E_HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; HE_HDL_st2, calibration of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HE_sbp, systolic blood pressure (mean value of 2–3 blood pressure measurements); HE_TG, triglyceride. Dyslipidemia, according to the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis, dyslipidemia is defined as any one of the following: total cholesterol level ≥ 240 mg/dL, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level < 40 mg/dL, triglyceride level ≥ 200 mg/dL, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level ≥ 160 mg/dL, or the use of a lipid-lowering drug; hypertension, according to Korean hypertension, hypertension was defined when systolic blood pressure was ≥ 140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure was ≥80 mmHg; Overweight/obesity, according to the Korean Society for the study of obesity; overweight/obesity defined when body mass index was 23 kg/m2 or higher; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellites according to the Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) T2DM was defined as fasting plasma glucose levels ≥ 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or glycated hemoglobin ≥ 6.5%.