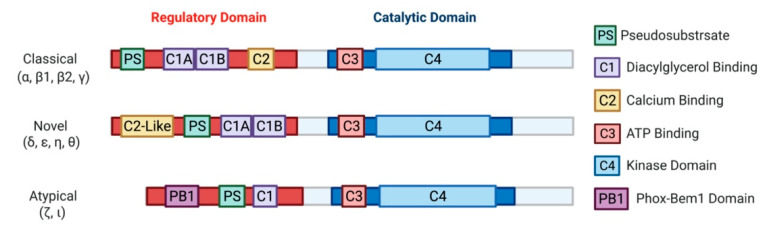
Figure 2.
A schematic representation of PKC subfamily structural domains. Distinct PKC isozymes are categorized into classical, novel, or atypical PKCs based on N-terminal regulatory domain structure and have conserved C1-4 domains. Classical PKC α, β1, β2, γ are activated by DAG and calcium through binding with C1A-C1B and C2 domain, respectively. Novel PKC isoforms δ, ε, η, θ are DAG dependent but calcium independent for their activation, as the C2-like domain cannot bind calcium. Atypical PKC ζ, ι do not respond to calcium or DAG. All PKC isozymes have a pseudosubstrate (PS) domain involved in kinase auto-inhibition. The C-terminal catalytic domain is highly homologous between all the PKC isozymes and consists of an ATP binding C3 domain and a C4 kinase domain.