Figure 6.
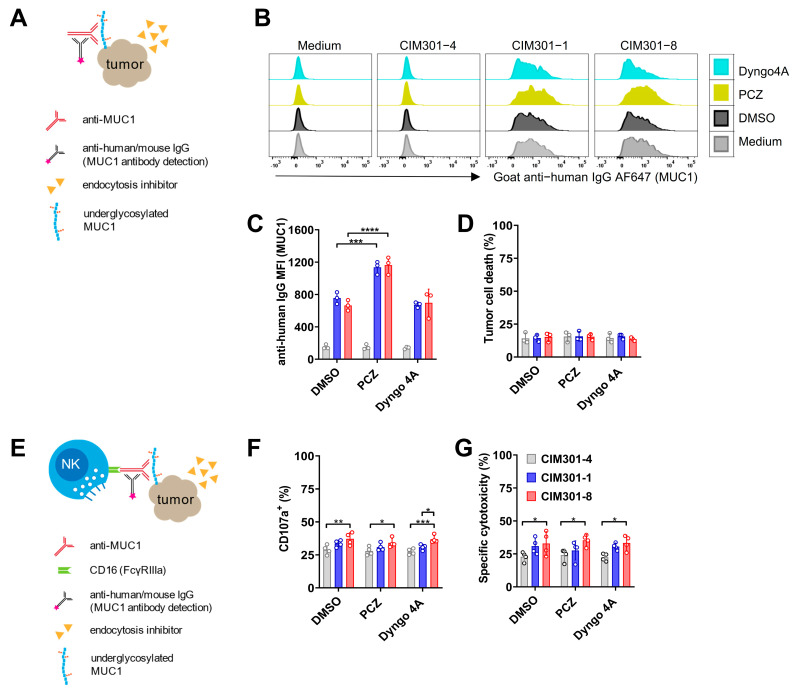
The endocytosis inhibitor PCZ promotes tumor antigen expression on T-47D cells but does not enhance antibody-dependent NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. (A) Experimental setup to determine whether endocytosis inhibitors enhance MUC1 epitope availability on tumor cells. (B) Overlay histograms of flow cytometric analysis of MUC1 epitope expression on T-47D tumor cells in the presence of endocytosis inhibitors using regular (CIM301-1) or defucosylated (CIM301-8) anti-MUC1 antibodies or an irrelevant control antibody (CIM301-4). Anti-human IgG antibodies were used to detect antibody binding on tumor cells. Endocytosis inhibitors were dissolved in DMSO, here used as a negative control. One representative sample is shown. (C) Flow cytometric quantification of MFI of MUC1 expression levels on T-47D cells after treatment with endocytosis inhibitors as described in (B). Differences between control antibody (CIM301-4; grey bars) and anti-MUC1 antibodies (regular CIM301-1 in blue and defucosylated CIM301-8 in red) were all statistically significant with p < 0.0001. (D) Viability of T-47D tumor cells after incubation with anti-MUC1 antibodies with or without endocytosis inhibitors. Pooled data from three independent experiments performed at different timepoints. (E) Schematic overview of assays to test whether endocytosis inhibitors influence NK cell degranulation and cytotoxicity in the presence of anti-MUC1 antibodies. (F) Fraction of CD107a+ degranulating human NK cells in co-cultures with T-47D tumor cells at an effector/target ratio of 1:1 in the presence of anti-MUC1 antibodies and endocytosis inhibitors. NK cells and tumor cells were incubated for 4 h, with endocytosis inhibitors (5 μM PCZ, 30 μM Dyngo4A and 0.1% (v/v) DMSO) added during the last hour. (G) Antibody-dependent NK-cell-mediated cytotoxicity against T-47D tumor cells. Experimental setup as in (F). Panels (F,G) show pooled data from four independent experiments with different donors, performed at different time points. Differences between groups were determined using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.05 (*); p < 0.01 (**); p < 0.001 (***); p < 0.0001 (****).