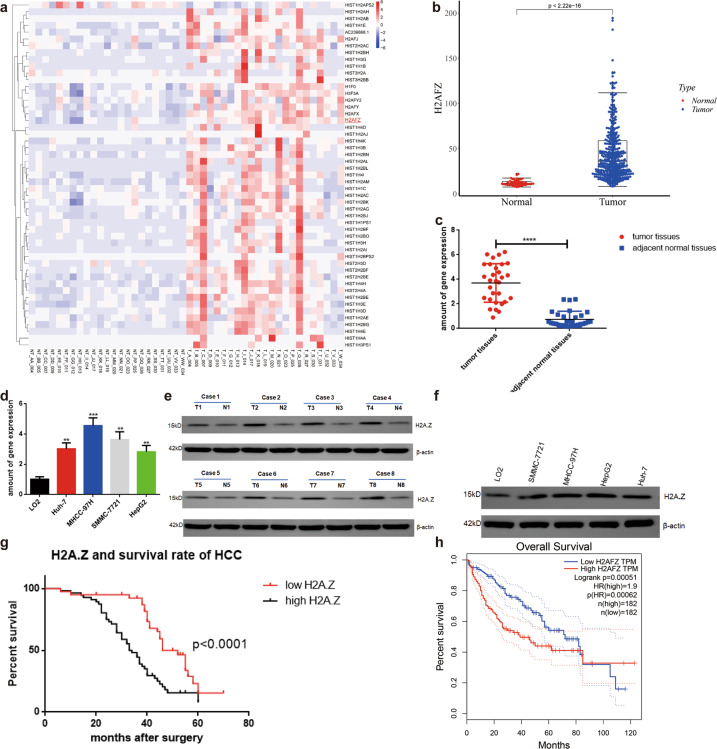
Fig. 1. H2A.Z is highly expressed in HCC tissues and cells and is associated with the prognosis in patients with HCC.
a Heat maps of histones and variants in 23 HCC and paired paracancer tissues analyzed using RNA-seq(Software: R pheatmap, Algorithm: ward2). b H2A.Z transcript between HCC tissues and normal liver tissues was analyzed in the publicly accessible samples(TCGA http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/; T = 375, N = 50)(Software: beeswarm, R package). c Scatter plots comparing H2A.Z expression in HCC samples and normal liver tissue samples detected by qPCR(Student’s t-test used in Fig c, n = 30 in each group). d The expression levels of H2A.Z in human HCC cells were detected by qRT-PCR. e Expression levels of H2A.Z protein were detected in 8 matched HCC samples by western blot (N, normal tumor-adjacent tissue; T, tumor tissue). f Expression levels of H2A.Z protein were detected in HCC cell lines by western blot. g Kaplan-Meier survival curves illustrating the overall survival and disease-free survival of patients with HCC associated with H2A.Z expression in 96 cases. h The negative correlation between H2A.Z expression and overall survival was analyzed on the basis of TCGA data in patients with HCC(Software: survival, R package). The data are expressed in terms of mean ± SD(Student’s t-test used in Fig d and Kaplan-Meier test used in Fig g; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; n = 3 in each group).