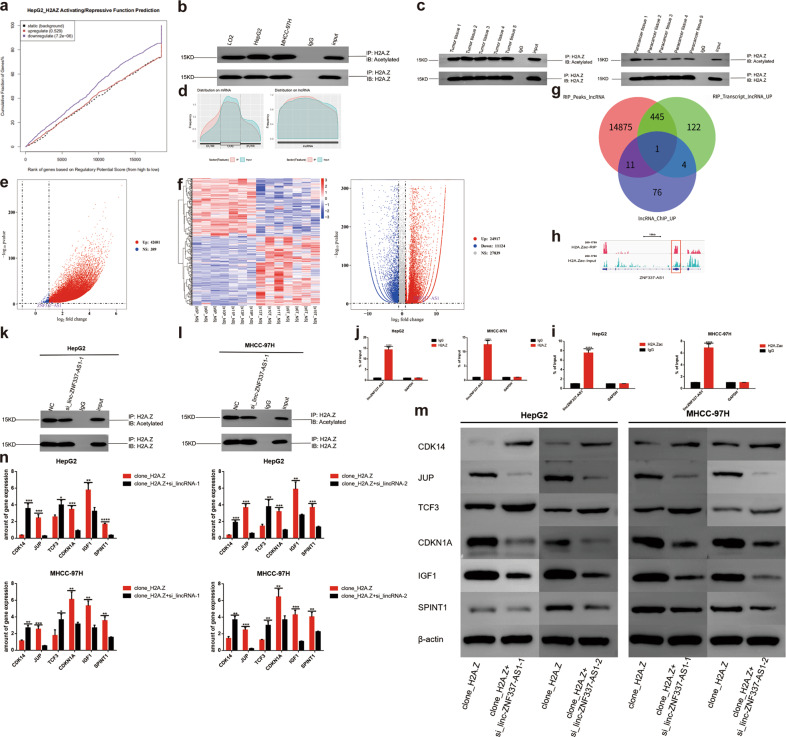
Fig. 5. LincZNF337-AS1 binds to H2A.Z and H2A.Zac, and regulates the acetylation of H2A.Z.
a H2A.Z mainly promoted the transcription of downstream genes(Software: BETA, algorithm: basic-k BSF-df 0.05). b The acetylation level of H2A.Z was detected by Co-IP in HCC cell lines. c The acetylation level of H2A.Z was detected by Co-IP in HCC tissues. d RIP with H2A.Zac antibody in HepG2 cells and sequencing. e Volcanograms of lincRNA identified by RIP-seq(Software: ggplot2, R package). f Heat maps and volcanograms of the seven pairs of HCC and paired paracancer tissues analyzed by RNA-seq(Software: R pheatmap, R package). g Venn diagram of RIP-seq and lincRNA highly expressed in tumors in RNA-seq. h IGV diagram of lincZNF337-AS1. i–j Identification of lincZNF337-AS1 binding to H2A.Z and H2A.Zac by RIP-qPCR. k–l LincZNF337-AS1 regulates the acetylation of HCC, the level of acetylation was measured by Co-IP. m, n QRT-PCR, and western blot verified the changes of downstream target genes after lincZNF337-AS1 knockdown in H2A.Z overexpressed HCC cell lines. The data are expressed in terms of mean ± SD (Student’s t-test used in Fig i, j, and n; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; n = 3 in each group).