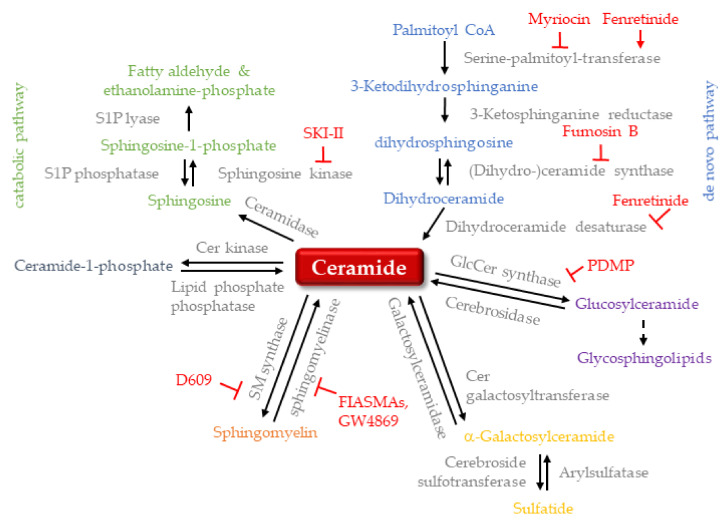
Figure 2.
Sphingolipid metabolism. Ceramide is the central hub of sphingolipid metabolism. De novo synthesis (blue) starts with palmitoyl CoA, and the salvage pathway starts with conversion to sphingosine and ends with a fatty aldehyde and ethanolamine-phosphate (green). The synthesis of glycosphingolipids starts with the formation of glucosylceramide (purple). Other key pathways are phosphorylation to ceramide-1-phosphate (blue-gray), conversion to sphingomyelin (orange) and glycosylation to α-galactosylceramide and sulfatide (yellow). Inhibitors of ceramide-metabolizing enzymes are shown in red. Cer: ceramide; GlcCer: glucosylceramide; S1P: sphingosine 1-phosphate; SM: sphingomyelin.