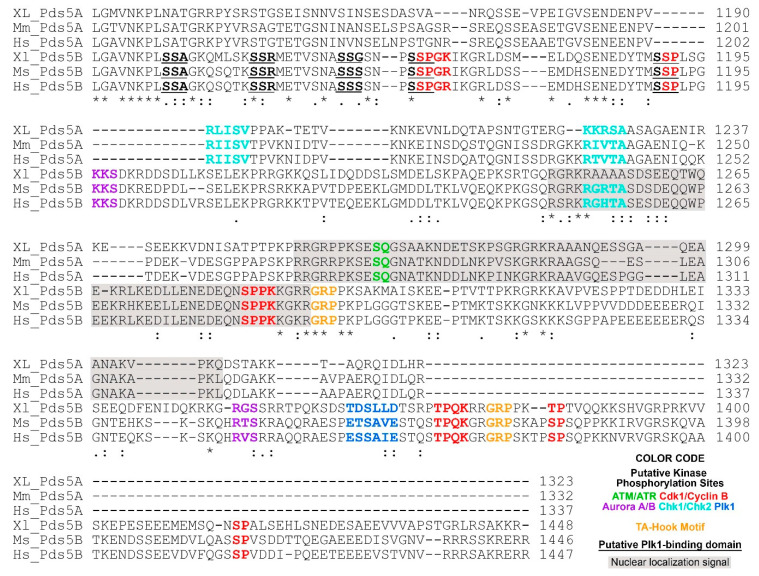
Figure 2.
C-terminal alignment of PDS5A and PDS5B from frog (Xenopus), mouse and human. The following putative regulatory features are highlighted in color: ATM/ATR phosphorylation motif (S/T)-Q [62]; Aurora A/B phosphorylation motif (R/K)1-3-X-(S/T)-(^P) where X is any amino acid, and ^P is not proline [63,64,65]; Cdk1/Cyclin B phosphorylation motif minimum consensus sequence (S/T)-P, full consensus sequence (S/T)-P-X-(K/R) [66]; Chk1/Chk2 phosphorylation motif (Φ/B)-(X/B)-(R/K)-X-X-(S/T)-Φ where B is a basic amino acid and Φ is a hydrophobic amino acid [67]; Plk1 phosphorylation motif (D/E)-X-(S/T)-Φ-X-(D/E). Plk1 binding domain (PBD) S-(pS/pT)-(P/X) where pS is a phosphorylated serine, pT is a phosphorylated threonine [68]. PBD is underlined. AT-hook motif GRP is highlighted in orange [69]. Nuclear localization signals are predicated using cNLS Mapper [70] and shaded in gray. The alignment was performed using Clustal O (1.2.4) [71]. Invariant, conserved and semi-conserved residues are indicated by an asterisk (*), colon (:) and period (.), respectively. The abbreviations are XL, Xenopus laevis; Mm, Mus musculus; Hs, Homo sapiens. Protein sequences are from NCBI and the access reference numbers are NP_001090063.1 (XL-PDS5A); NP_001089658.1 (XL-PDS5B), NP_001074790.1 (Mm-PDS5A), NP_780519.3 (Mm-PDS5B), NP_001093869.1 (Hs-PDS5A), NP_055847.1 (Hs-PDS5B).