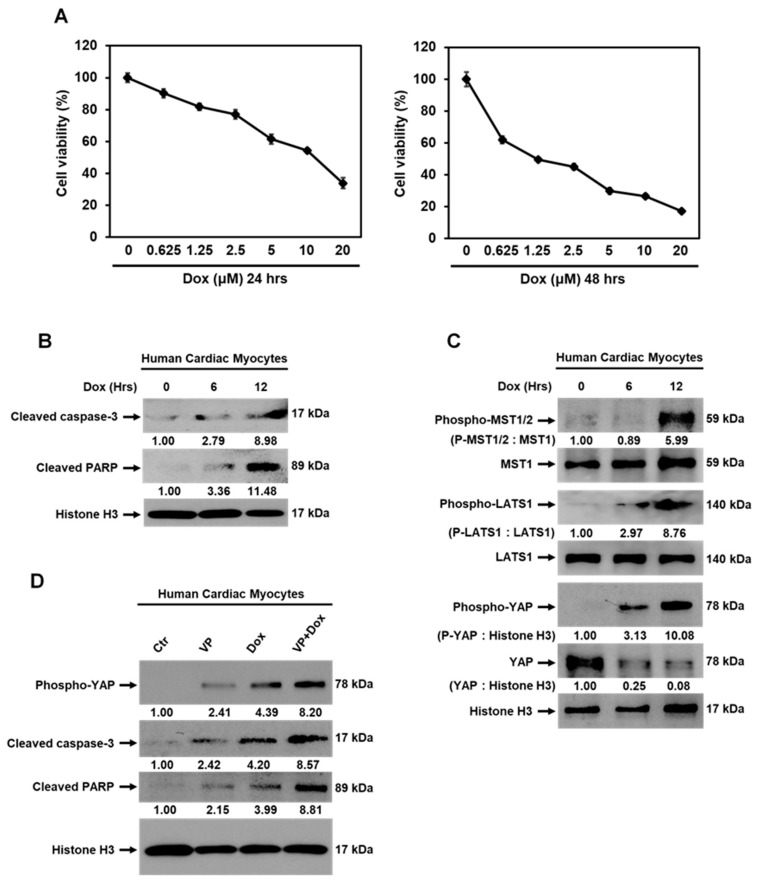
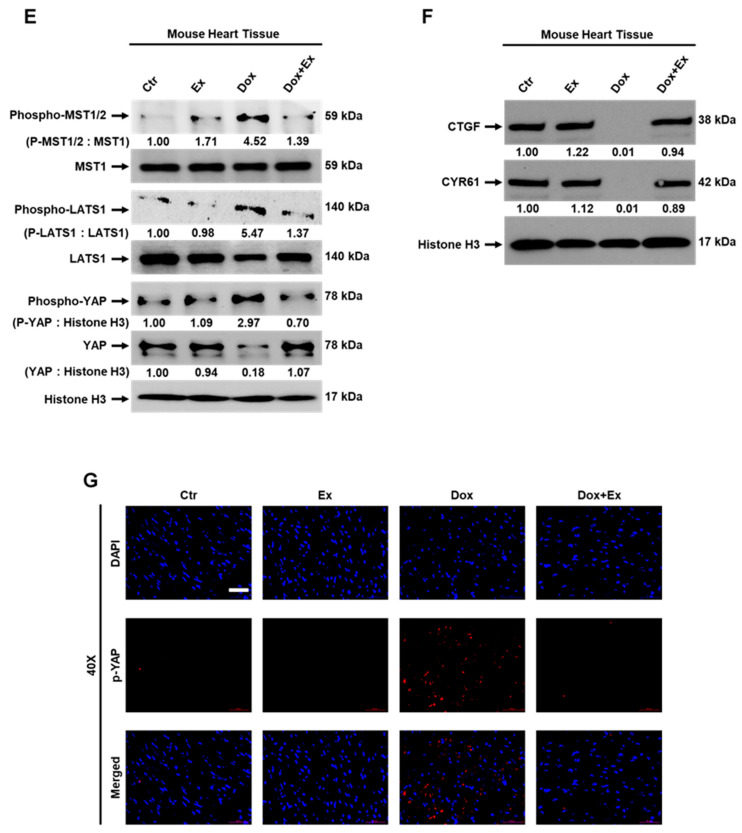
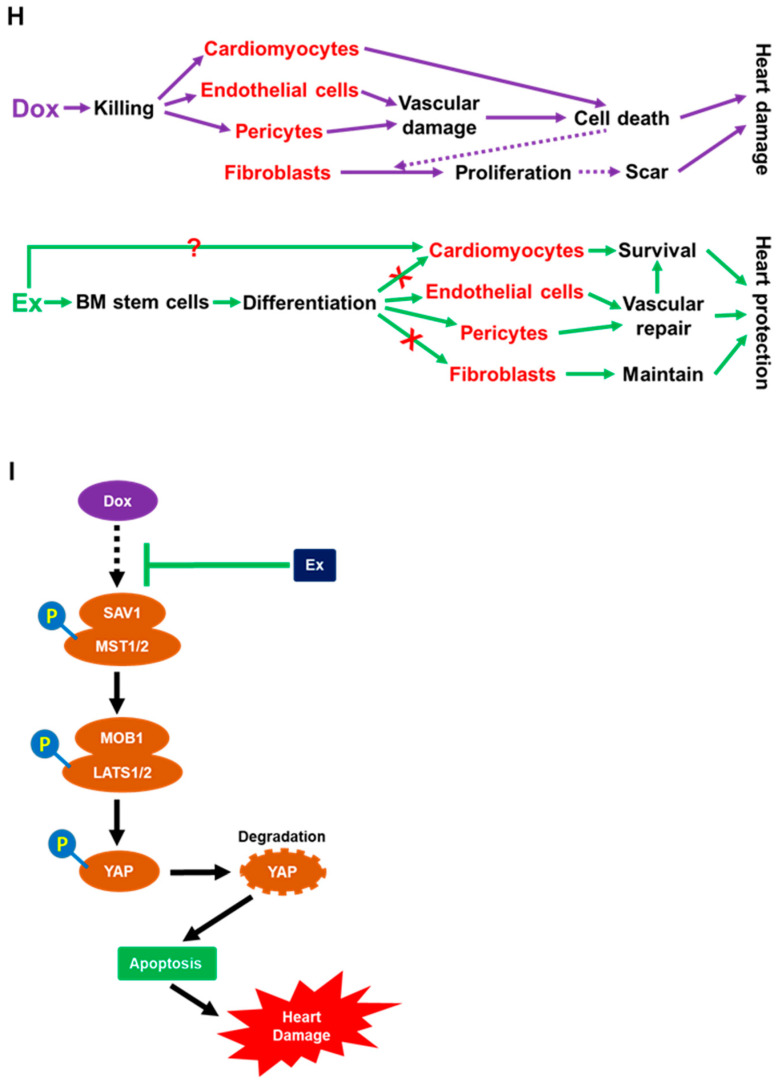
Figure 8.
Activation of Hippo-YAP signaling is induced by Dox therapy. (A) MTT assay analysis for viability of human cardiac myocytes (HCMs) treated with various concentrations of Dox as indicated for 24 or 48 h. Values represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (B) Western blot analysis for cleaved caspase-3, cleaved PARP, and histone H3 expression in HCMs treated with Dox at 1.25 µM for 0, 6, or 12 h. (C) Western blot analysis of phospho-MST1/2, MST1, phospho-LATS1, LATS1, phospho-YAP, YAP, and histone H3 expression in HCMs treated with Dox at 1.25 µM for 0, 6, or 12 h. (D) Western blot analysis of phospho-YAP, cleaved caspase-3, cleaved PARP, and histone H3 expression in HCMs treated with mock (control), verteporfin (VP) at 2.5 µM, Dox at 1.25 µM, or combination of VP with Dox for 8 h. (E,F) Western blot analysis of phospho-MST1/2, MST1, phospho-LATS1, LATS1, phospho-YAP, YAP, histone H3 (E), CTGF, CYR61, and Histone H3 (F) expression in hearts from Ctr, Ex, Dox, and Dox+Ex group mice. (G) Representative immunofluorescence images of heart sections stained for DAPI (blue) and p-YAP (red) from Ctr, Ex, Dox, and Dox+Ex group mice. Magnification, 40×; Scale bar, 50 µm. (H,I) Summary of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of Ex-mediated protection of Dox-induced cardiotoxicity as described in Section 4. Ex, exercise; Dox, doxorubicin; VP, verteporfin; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; CYR61, cysteine-rich angiogenic inducer 61.