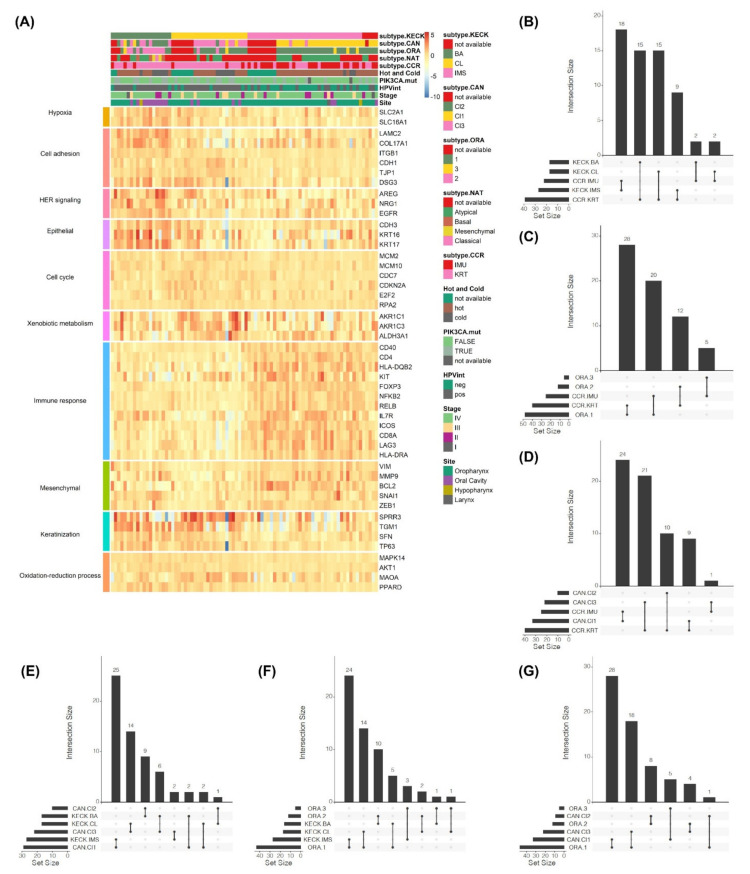
Figure 1.
Comparison of the different definitions of HPV-positive head and neck subtypes: (A) Heatmap illustrating expression of genes and pathways previously identified as distinguishing HPV(+) subtypes; genes and pathways were combined from Keck et al. (KECK) and Zhang et al. (CCR) subtype findings, and visualized using log2FPKM values normalized (mean centered) by genes and samples. Additionally, shown are several annotations which indicate trends among subtypes and with tumor characteristics. KECK subtypes were re-designated for all 66 TCGA and 18 UM HPV(+) cases by applying their algorithm, while all other subtype definitions were obtained directly from the original publications. (B–G) Upset plots illustrating pairwise overlaps among subtype definitions: (B) KECK (BA/CL/IMS) vs. CCR (IMU/KRT), (C) ORA (1/2/3) vs. CCR (IMU/KRT), (D) CAN (Cl1/Cl2/Cl3) vs. CCR (IMU/KRT), (E) CAN (Cl1/Cl2/Cl3) vs. KECK (BA/CL/IMS), (F) ORA (1/2/3) vs. KECK (BA/CL/IMS) and (G) ORA (1/2/3) vs. CAN (Cl1/Cl2/Cl3).