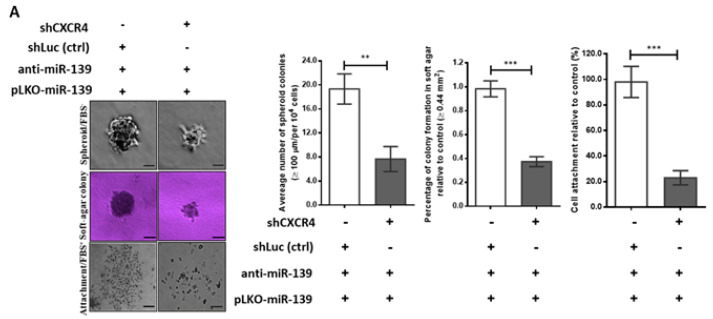
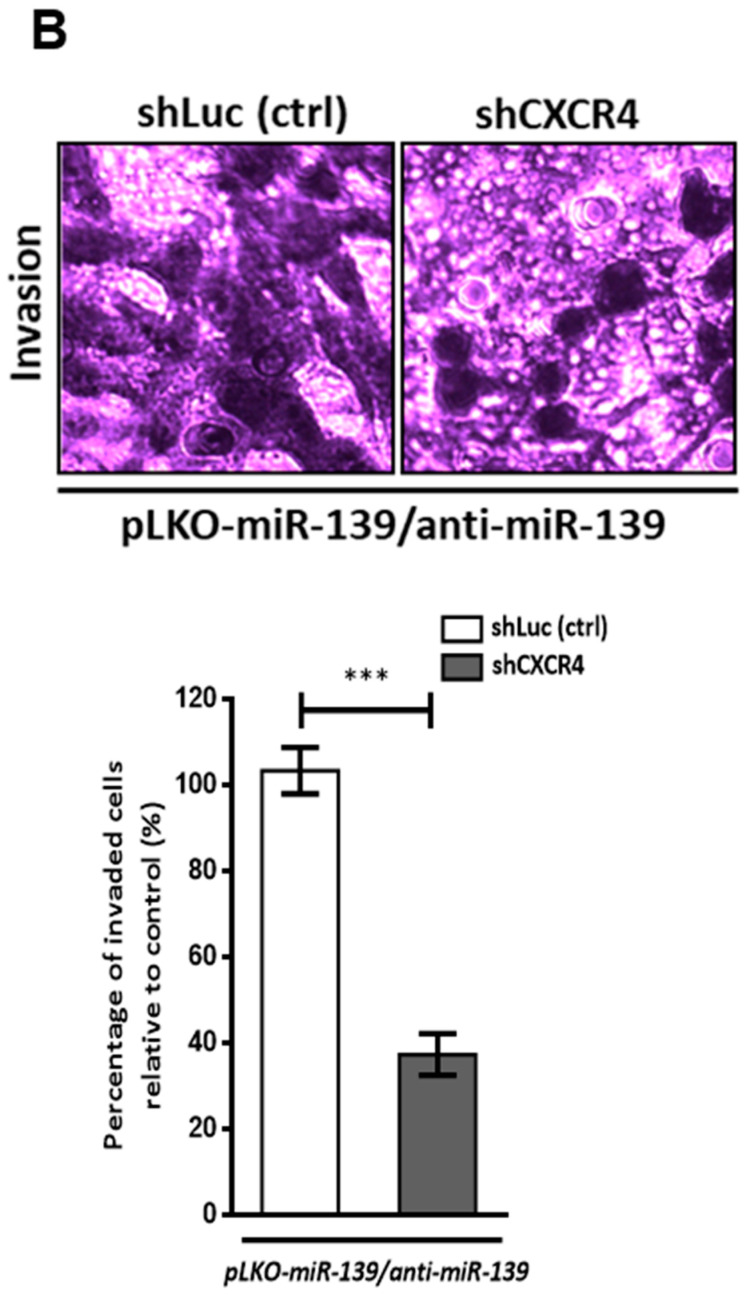
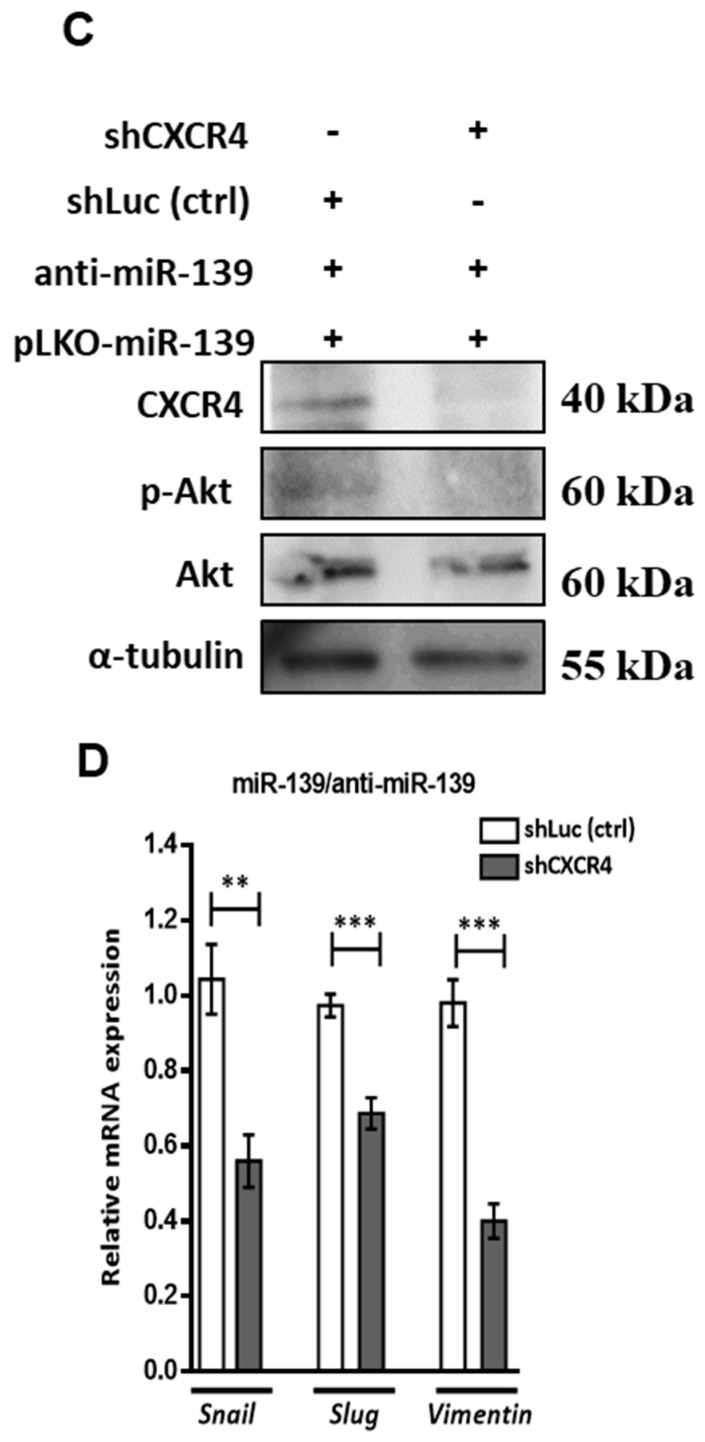
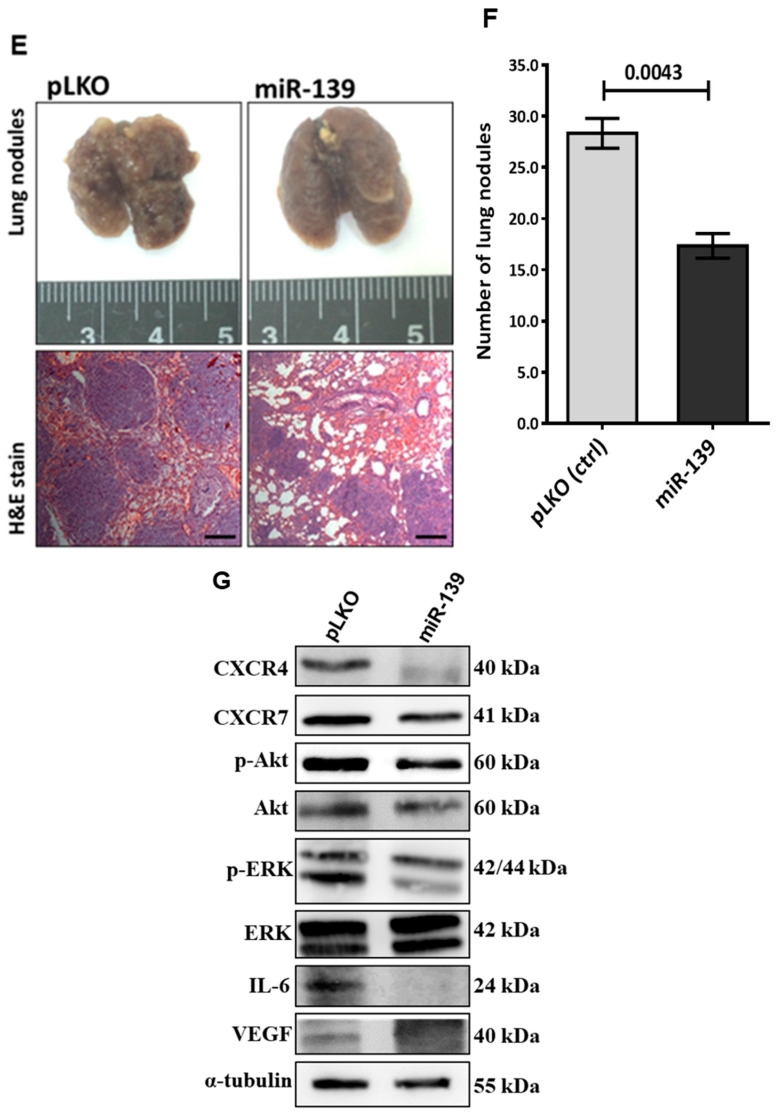
Figure 5.
MiR-139 inhibits breast cancer cell stemness and metastatic lung colonization of breast cancer xenografts via down-modulation of CXCR4. (A) Representative images and histograms show the stemness characteristics, including the spheroid cell aggregation, colony formation in soft agar, and cell attachment behavior in MDA-MB-231 cells treated as indicated. Scale bar, 50 µm. (B) Representative photos of Boyden chamber assay. Invasion capacity was assessed in BCSCs carrying pLKO-miR-139 co-transfected with miR-139 inhibitor and the negative control [shLuc (ctrl)] or shCXCR4, as indicated. cancer cells transfected with different shRNAs as indicated. (C) Western blot results of CXCR4, p-Akt, and Akt in BCSCs carrying pLKO-miR-139 co-transfected with miR-139 inhibitor in combination with different shRNAs as indicated. (D) Histograms show mesenchymal markers (Snail, Slug, and vimentin) in MDA-MB-231/pLKO-miR-139 cells co-treated with miR-139 inhibitor (anti-miR-139) and different shRNAs as indicated. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (E) Representative lungs and HE staining of metastatic tumor lung tissues from mice five weeks after tail vein injection of MDA-MB-231 cells carrying miR-139 or pLKO vector (control) are shown. Scale bar, 100 µm. (F) Number of metastatic nodules in lungs of mice (n = 5 per group). (G) Five weeks post-xenotransplantation, lung tumors were excised and sectioned. Western blot analysis of the proteins of interest examined in lung tumors carried pLKO-miR139/MDA-MB-231 cells or control group as shown. α-tubulin was used as an internal control.