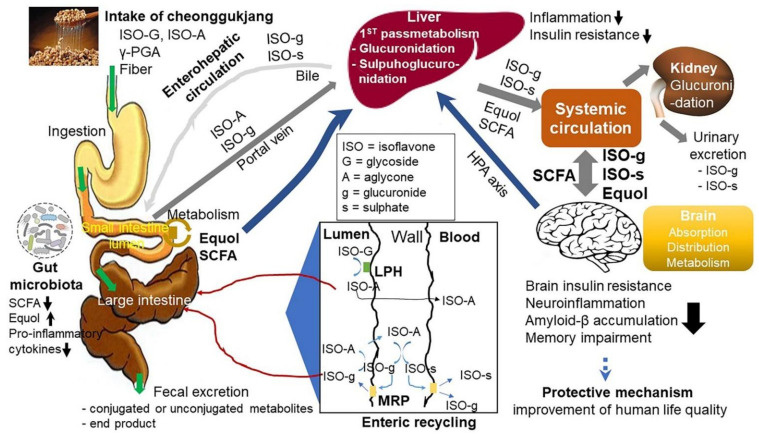
Figure 4.
Potential mechanism of CGJ in memory function. The boxed panel contains a schematic diagram representing the metabolism of isoflavones in the intestine. Soybean-fermented CGJ components actively influence cellular metabolism in the liver and brain, exerting positive effects through the gut–intestine–microbiome–liver–brain axis. Improved cellular metabolism in the hippocampus decreases β-amyloid accumulation, insulin resistance, neuroinflammation, and memory impairment in the brain. This result suggests that a diet containing CGJ, in part, protects against type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and post-stroke symptoms [3,63]. ISO, isoflavone; ISO-A, isoflavone aglycone; ISO-G, isoflavone glycoside; ISO-g, isoflavone glucuronide; ISO-s, isoflavone sulfate; sHPA-axis, short hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis; LPH, membrane-bound lactase phlorizin hydrolase; MRP; (multi-drug resistance-related protein); γ-PGA, poly-γ-glutamic acid; SCFA, short-chain fatty acids. Figure adapted from Jeong, D.Y. et al. [3] and Larkin, T. et al. [63].