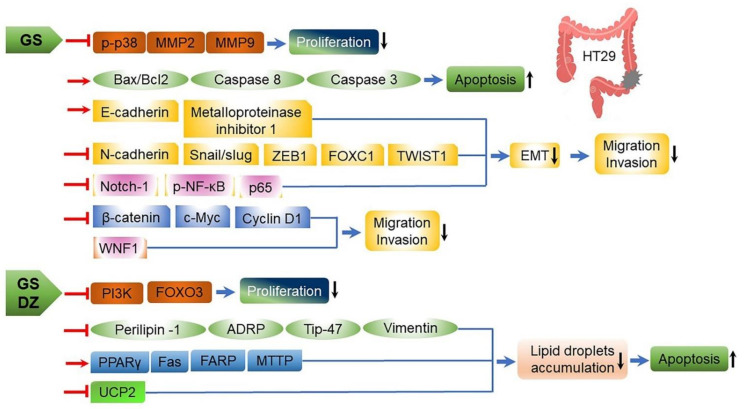
Figure 6.
The mechanism of daidzein (DZ) and genistein (GS) regulation at transcriptional and translational levels in HT29 colon cancer cells. GS represses expression of phosphorylated p38 (p-p38), and matrix metalloproteinases (MMP2 and MMP9) to inhibit HT29 cell proliferation, upregulates Bax/Bcl-2, caspase-8, and caspase-3 activity to enhance HT29 cell apoptosis, reverses epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) through regulation of EMT markers and regulates Wnt signaling pathways by increasing Wnt inhibitory factor 1(WIF1) to block HT29 cell migration and invasion. Additionally, DZ and GS inhibit expression of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) to suppress HT29 cell proliferation and decrease lipid droplet accumulation to provoke HT29 cells apoptosis [9]. ADRP, adipose differentiation-related protein; Bax2, apoptosis regulator belonging to Bcl2 family; Bcl2, anti- or pro-apoptosis regulator; c-Myc, multifunctional transcriptional factor; FARP1, RhoGEF and pleckstrin domain-containing protein 1; Fas, fatty acid synthetase; FOXC1, forkhead box C1; MMP2; matrix metalloproteinase 2; MTTP, microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; Notch-1, member of type 1 transmembrane protein family; p65 (RELA), transcription factor 65; p-NF-κB, phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa B; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma; Snail/Slug, master regulatory transcription factor; Tip-47, lipid droplets-associated protein; TWIST, time without symptoms of diseases and subjective toxic effects of treatment; UCP2, uncoupling protein 2; ZEB, zinc-finger E-box-binding homeobox protein as a transcription factor; ↑, induction; ↓, repression; →, activation; ˧, inhibition. Figure adapted from Hsiaoa, L.H. et al. [9].