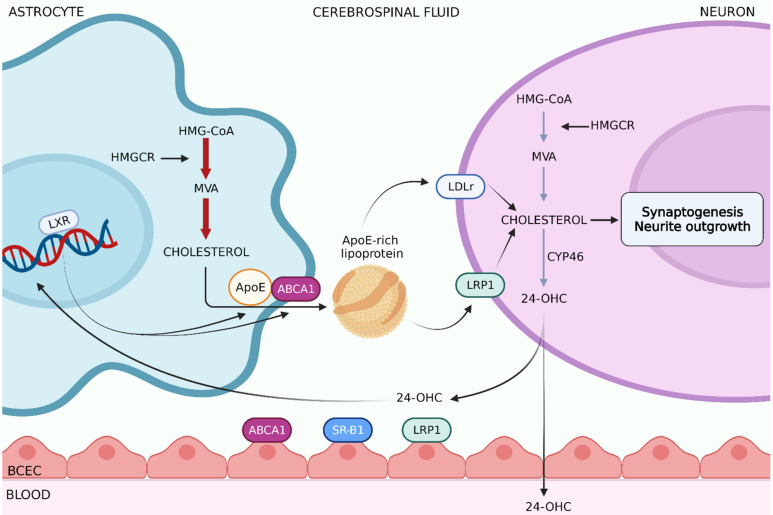
Figure 2.
Cholesterol metabolism in the CNS. Cholesterol in the brain is assured by de novo biosynthesis requiring a multistep pathway. HMGCR is responsible for the conversion of HMG-CoA in MVA and represents the key and rate-limiting step. In the adult CNS, neurons reduce their own cholesterol synthesis and import this lipid from astrocytes, which secrete apoE rich-lipoproteins through ABCA1 transporters. ABCA1 and apoE transcription is elicited by LXR, whose activity is modulated by 24-OHC. Cholesterol uptake in neurons is ensured by LDLr and LRP1, particularly expressed on the cell membranes of neurons. Cholesterol excretion in the brain is mainly promoted by its conversion to 24-OHC catalyzed by CYP46. Abbreviations: 24-OHC, 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; apoE, apolipoprotein E; BCEC, brain capillary endothelial cells; CYP46, cholesterol 24-hydroxylase; HMGCR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; LDLR, LDL receptor; LRP1, LDLr-related protein 1; LXR, liver X receptor; MVA, mevalonate; SR-B1, scavenger receptor class B member 1. This figure is created with BioRender.