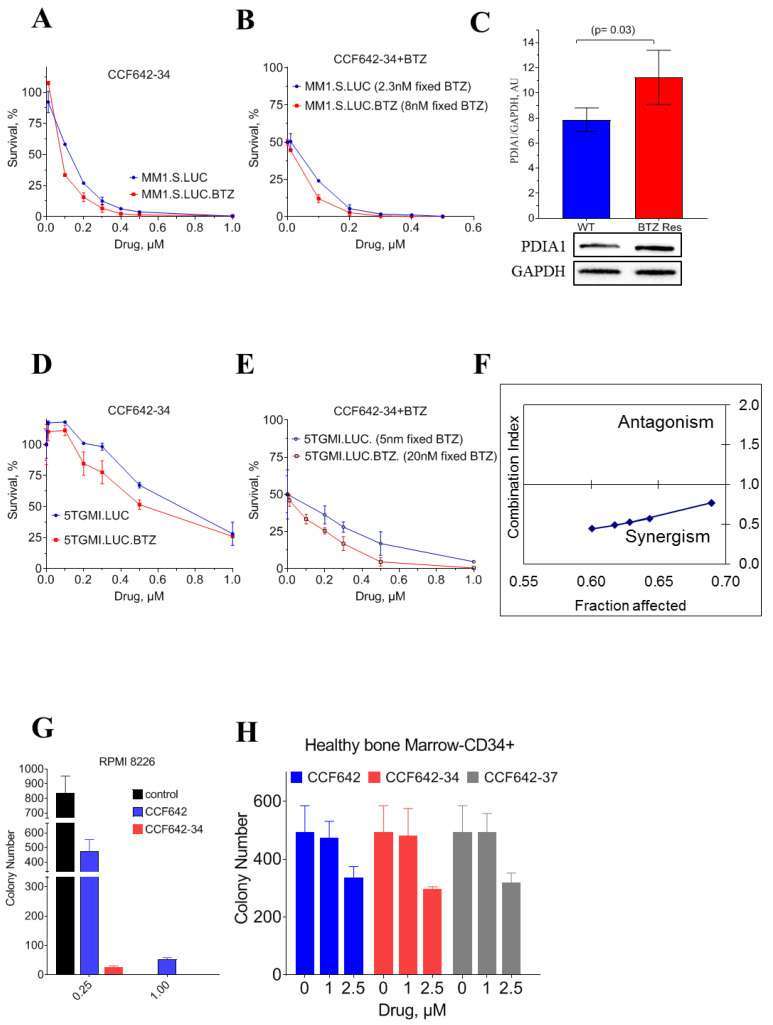
Figure 3.
Selective cytotoxicity of PDIA1 inhibitor against multiple myeloma MM1.S cells. Cell viability and LD50 for inhibitors were measured in 96 well culture plates (2 × 104 cells/well) after 72 h of treatment using CellTiter-Glo® Luminescent Cell Viability Assay (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). (A) Cell survival assay with MM1.S.luc and BTZ-resistant MM1.S.luc cells. (B) Bortezomib was used at a fixed IC50 concentration of 2 nM for MM1.S.luc, 8 nM for MM1S.luc BTZ for combined drug toxicity analysis. (C) Comparison of PDIA1 protein levels in MM1.S.luc and MM1.S.luc BTZ-resistant cells. Band intensity was calculated with Image Lab Version 5.2.1. (D) Cell survival assay with 5TGM1.luc and (E) BTZ-resistant 5TGM1.luc cells. (F) MM1.S cell line was exposed to CCF642-34, and BTZ for 72 h for synergistic drug combination test according to Chou and Talalay method. If the fraction of cells affected remained less than 1, the two drugs were determined as synergistic. (G,H) Toxicity of CCF642 and its analogues, CCF642-34 and CCF642-37, against RPMI 8226 and CD34+ normal bone marrow cells from healthy individuals in a colony-forming assay. The number of colony-forming units were plotted for each treatment. The toxicity against normal bone marrow was estimated at ~20-fold over the drugs against multiple myeloma cells.