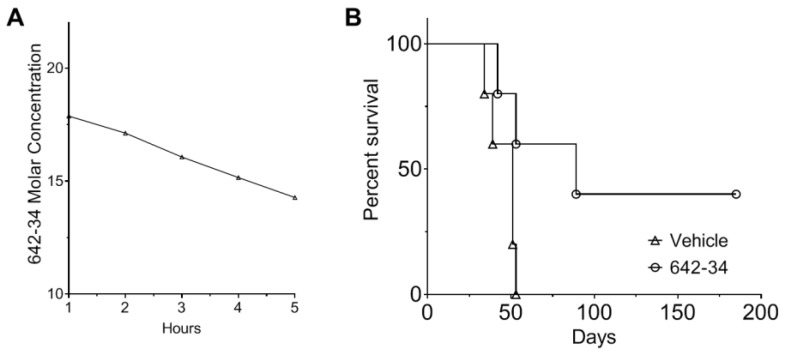
Figure 6.
Stability of CCF642-34 and restriction of multiple myeloma in a syngeneic mouse model by PDIA1-inhibitor CCF642-34. (A) The stability of CCF642-34 was measured against oxidative metabolism by human liver microsomes. CCF642-34 (20 µM) was incubated with 0.25 mg/mL of human liver microsomes for 5 h. The residual compound at indicated time points was measured by HPLC (Agilent 1260 Infinity II) interfaced with reverse phase C18 column using 280 nm and 245 nm detection wavelength. The standard curve of known concentrations of CCF642-34 was obtained from the area under the peak at two wavelengths, and the remaining CCF642-34 was estimated. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (B) 5TGM1-luc/C57BL/KaLwRij mouse models of myeloma (3 males, 3 females per treatment group) were engrafted with 2 × 106 5TGM1-luc cells via tail vein injection and treated 3 times a week for 8 weeks per oral gavage with 20 mg/kg of CCF642-34 dissolved in 10% 2-hydroxy-propyl-β-cyclodextrin. The survival of each group was monitored, and Kaplan–Meier survival analysis was performed. All control animals required euthanasia before 52 days (due to paraparesis, weight loss, poor general condition), while 3 out of 6 mice treated with CCF642-34 lived beyond 6 months with no sign of disease.