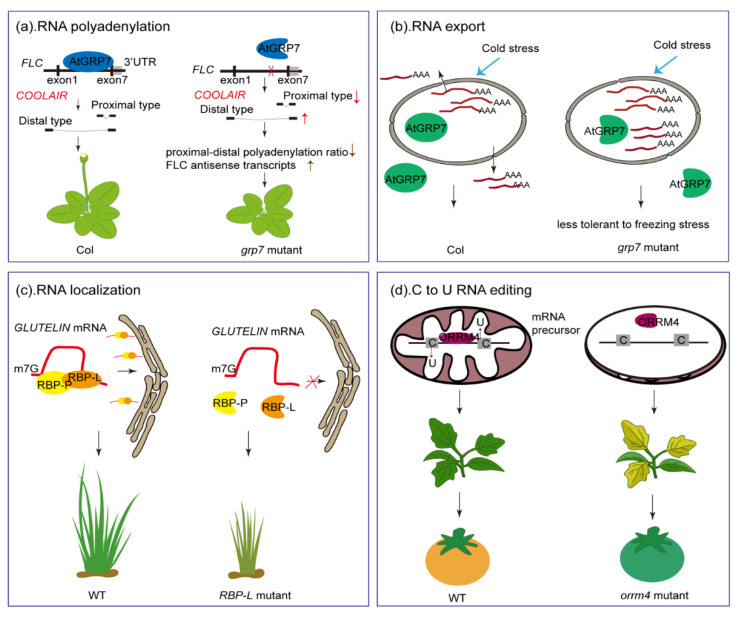
Figure 3.
Cellular functions of diverse GR-RBPs involved in RNA metabolism during plant growth, development and stress responses. (a) AtGRP7 affects the polyadenylation site usage of COOLAIR transcripts, leading to an altered ratio of proximally–distally spliced variants. Loss of AtGRP7 function leads to increased abundance of FLC antisense transcripts and a reduced proximal–distal polyadenylation ratio, resulting in late flowering compared with the wild type. (b) AtGRP7 is located in the nucleus and cytoplasm and is involved in mRNA export from the nucleus to the cytoplasm under cold stress conditions. In grp7 mutants, the export of mRNA is impaired, leading to its accumulation in the nucleus, while mRNAs transcribed in the nucleus are efficiently exported to the cytoplasm in wild-type plants subjected to cold stress. (c) An insertional allele in rice, RBP-L, causes growth defects due to the loss of RBP and the consequent mislocalization of GLUTELIN target RNA. (d) Knocking out the mitochondrial RNA editing factor ORRM4 in tomato causes defective mitochondrial editing, leading to yellowish seedlings and delayed fruit ripening.