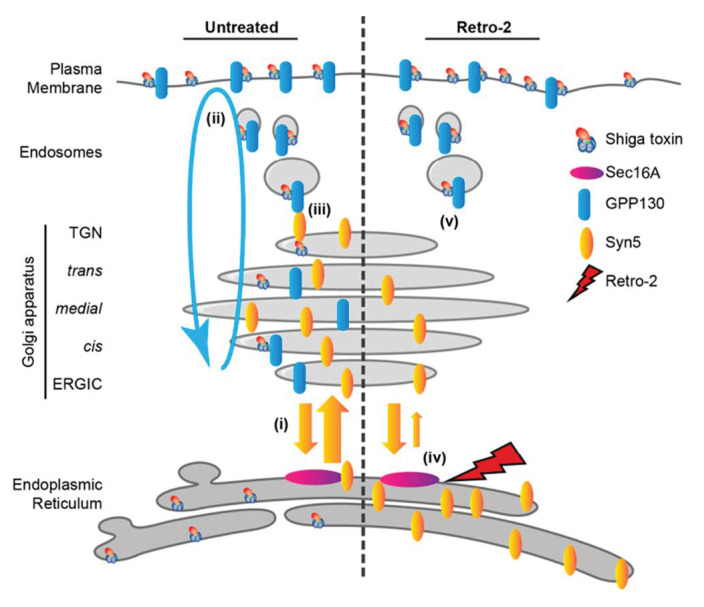
Figure 7.
Model of how Retro-2 induces a block of Shiga toxin trafficking at the level of early endosomes. In untreated conditions (left), Shiga toxin trafficking from early endosomes to the TGN requires the interaction of GPP130 (blue) with syntaxin-5 (Syn5, yellow). From the TGN, Shiga toxin then moves on to the ER from where the catalytic A-subunit is translocated to the cytosol to inactivate ribosomes. Under Retro-2 treatment conditions (right), the anterograde transport of syntaxin-5 between ER and Golgi is slowed down by the interaction of Retro-2 with Sec16A, leading to the partial depletion of syntaxin-5 in the Golgi, a loss of its interaction with GPP130, and thereby the blockage of STxB in early endosomes. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [70].