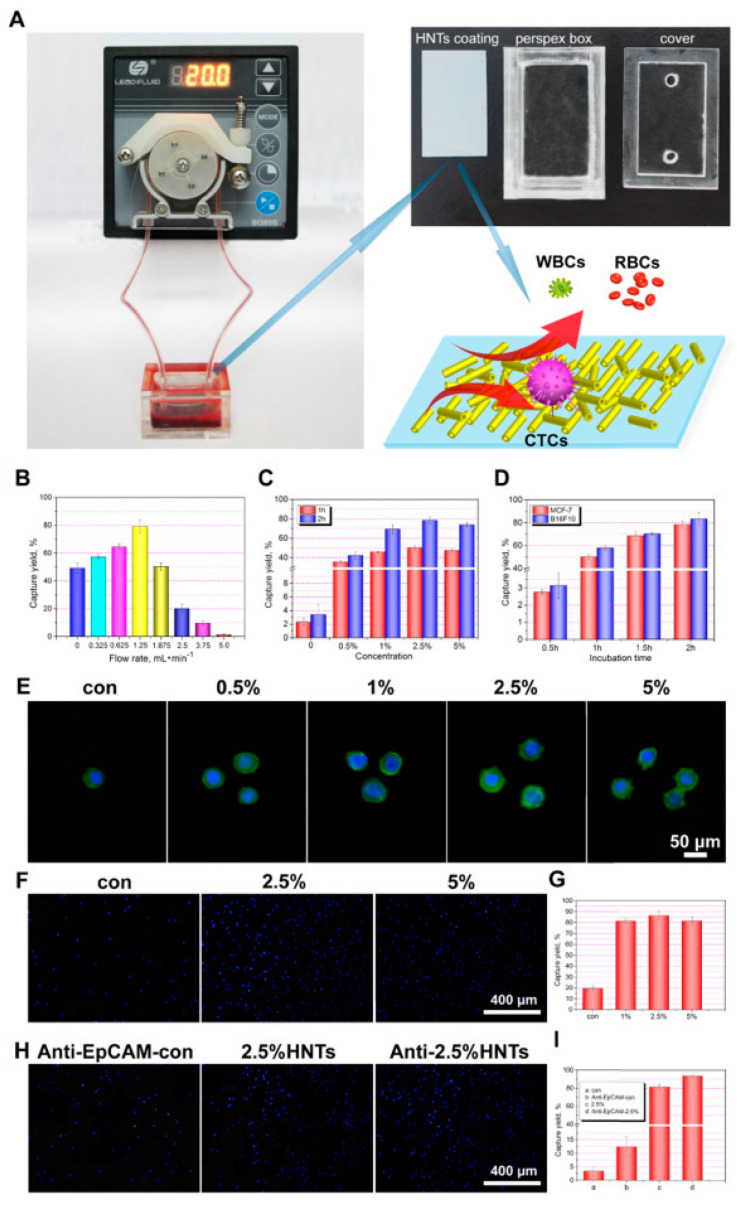
Figure 5.
The photo of a circulating device with a peristaltic pump and the schematic diagram of cell capture from whole blood (A). The capture yield to MCF-7 cells with different flow rate (B). The capture yield to MCF-7 cells with different rough HNTs coating surfaces (C). The capture yield to MCF-7 cells at different times (D). The Alex Flour 488 and DAPI stained fluorescence microscopy images of captured cells of MCF-7 on the different coatings for 2 h (E). The DAPI stained fluorescence microscopy images showing that the MCF-7 cells captured by different coating surfaces under dynamic shear conditions for 1 h and then standing for another 2 h (F) and quantification of the captured MCF-7 (G). The DAPI stained fluorescence microscopy images of the MCF-7 cells captured by smooth glass and 2.5% HNT coating without and with anti-EpCAM conjugation for 2 h at a flow rate of 1.25 mL·min−1 (H) and the cell capture yield (I). Reprinted from Materials Science & Engineering C, Vol 85, Rui He, Mingxian Liu, Yan Shen, Rong Liang, Wei Liu, Changren Zhou, Simple fabrication of rough halloysite nanotubes coatings by thermal spraying for high performance tumor cells capture, Pages 170–181., Copyright (2018), with permission from Elsevier [47].