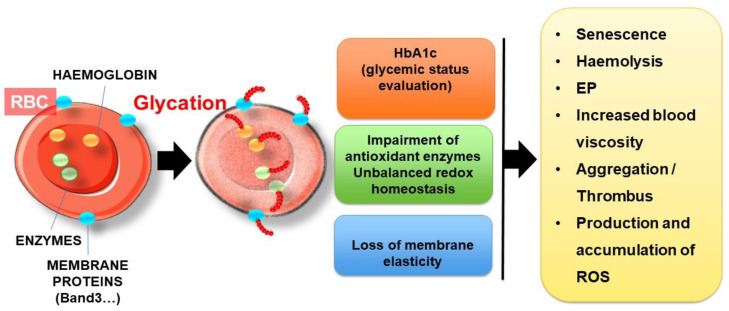
Figure 8.
Deleterious effects of erythrocyte glycation. Hyperglycaemia causes glycation of many RBC components, such as haemoglobin, antioxidant enzymes and cell surface membrane proteins. This phenomenon induces unbalanced redox homeostasis with the loss of membrane elasticity. As a consequence, erythrocyte senescence, haemolysis, EP, erythrocyte aggregation and ROS production are enhanced.