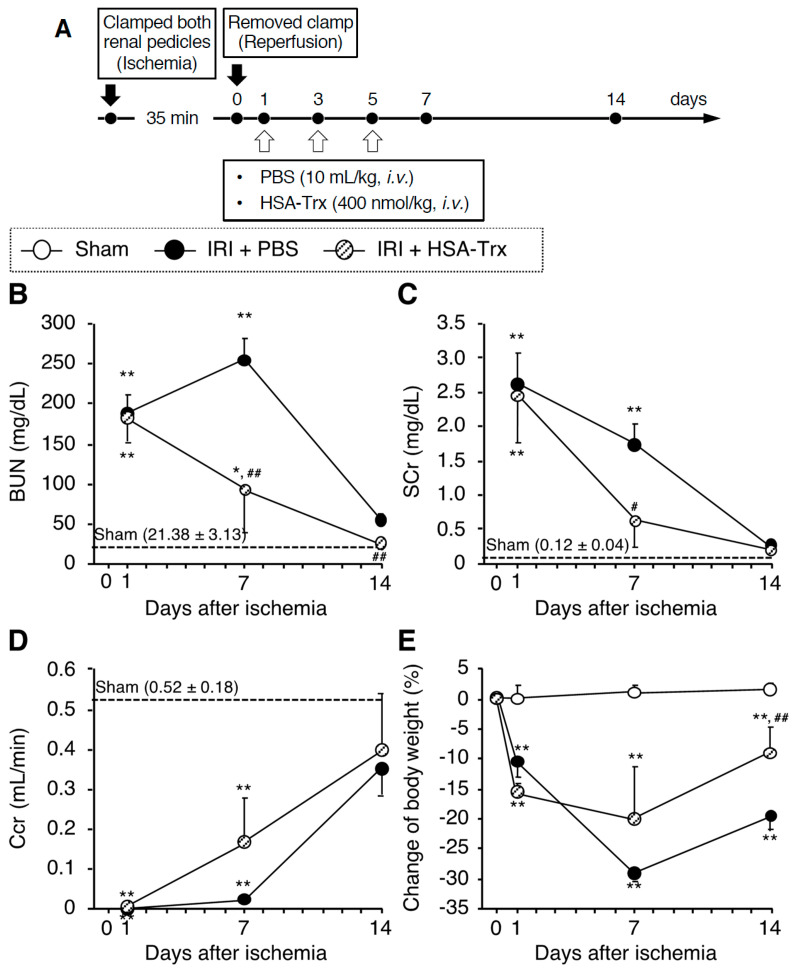
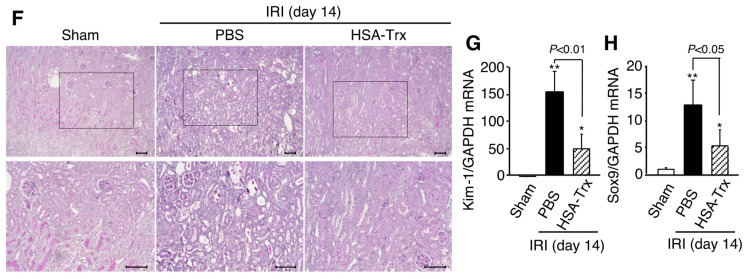
Figure 1.
Renoprotective effect of HSA-Trx against AKI to CKD transition. (A) Experimental protocol for the effective evaluation of HSA-Trx on renal IR-induced AKI to CKD transition model mice: The mouse model of AKI to CKD transition was induced by renal IR where both renal pedicles were clamped for 35 min. HSA-Trx (400 nmol/kg) was administered intravenously on 1, 3 and 5 days after renal IR. An equivalent amount of PBS (10 mL/kg) was administered to the sham operation group and the renal-IR group. The mice were sacrificed 14 days after IR. (B) Blood urea nitrogen (BUN), (C) serum creatinine (SCr) and (D) creatinine clearance (Ccr) were measured at 1, 7 and 14 days after renal IR. (E) Percent change in body weight from the baseline (before renal IR). Data are expressed as the mean ±SD (n = 5). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with sham mice at each time point. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 compared with renal IR-mice administered with PBS at each time point. Effect of HSA-Trx against renal tubular damage in renal IR-treated mice 14 days after IR: (F) Representative photomicrographs of Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS)-stained kidney sections are shown for 14 days after renal IR. Lower panels are an enlarged image of the upper panel. Original magnifications: ×200 (upper panels); ×400 (lower panels). Scale bars represent 100 μm. mRNA expression of (G) Kim-1 and (H) Sox9 in kidney on 14 days after renal IR were determined by real-time PCR. Data are expressed as means ±SD (n = 5). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with sham mice.