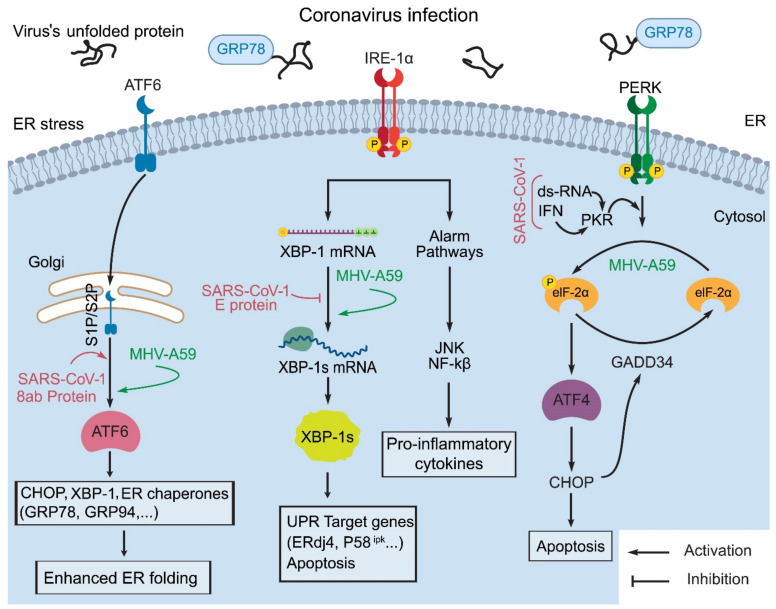
Figure 3.
Induction of three ER stress sensors during coronavirus infection. This activation can affect coronavirus folding, transportation, and degradation as well as apoptosis induction in prolonged circumstances. The SARS-1 and MHV-A59 infections mainly trigger the phosphorylation of eIF2α, mostly by PKR and PERK activation. The IRE1 activation mediates XBP-1 splicing and consequently induces UPR genes such as ERdj4 and p58IPK (58 kDa inhibitor protein kinase), which is inhibited by the SARS-1 E protein. Finally, ATF6 is processed by Site-1 protease (S1P) and Site-2 protease (S2P). ATF6 activation also increases the folding capacity of the ER, which has been verified in the MHV-A59 infection model, and the transfection of SARS-1 8ab protein. eIF2: eukaryotic initiation factor 2; PERK: protein kinase R (PKR)-like ER kinase; IRE1: inositol-requiring enzymes; XBP1: X-box binding protein; ATF6: activating transcription factor 6; GRP78: glucose-regulated protein 78; ATF4: activating transcription factor 4; ERdj4: ER-localized DnaJ 4; p58IPK: 58 kDa inhibitor protein kinase; S1P/S2P: Site-1 protease/Site-2 protease; IFN: interferon; GADD34: growth arrest and DNA damage inducible protein 34.