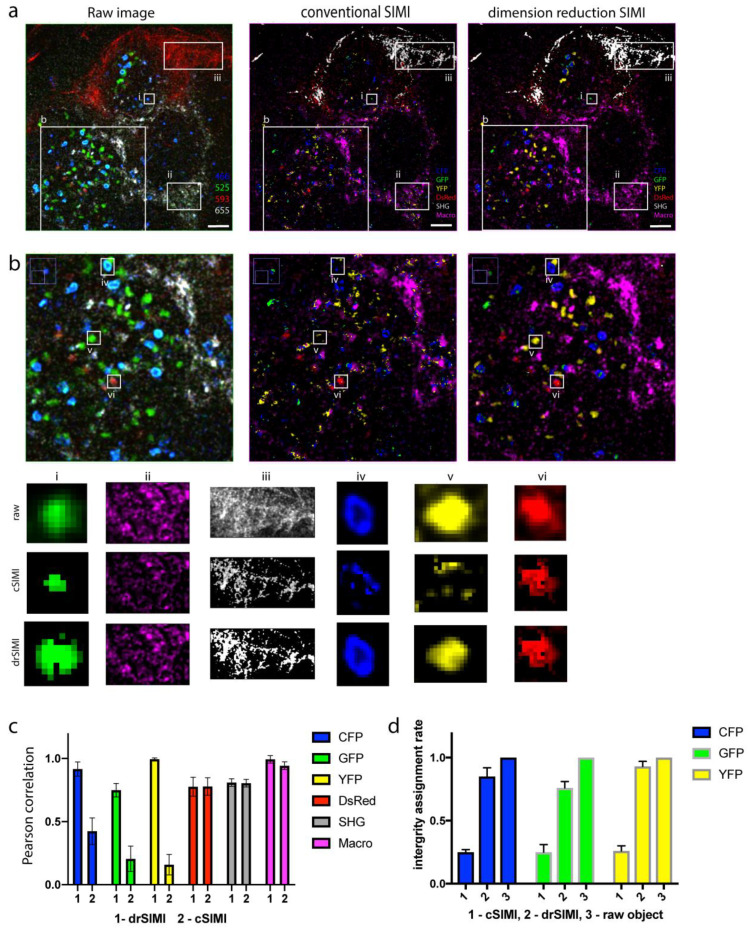
Figure 3.
Comparison of unmixing performance between the cSIMI approach and the drSIMI unmixing. (a) Raw image, cSIMI unmixed, and drSIMI processed images of a popliteal lymph node from a fluorescent reporter mouse. Color coding: (raw image) blue—PMT channel 466, green—PMT channel 525, red—PMT channel 595, grey—PMT channel 655; (SIMI conventional and block reduction) blue—cyan fluorescent protein (CFP), green—enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP), yellow—yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), red—red fluorescent protein isolated from Discosoma (DsRed), grey—second harmonics generation (SHG), magenta—macrophages (autofluorescence). (b) Zoom-ins from (a) show clearly better unmixing performance of the drSIMI approach compared to the cSIMI approach. Field of view of each unmixed compartment, chosen for colocalization analysis. (c) Quality control of unmixing performance of drSIMI and cSIMI unmixing based on Pearson correlation coefficient. (d) Quantification of the unmixing performance: graph of integrity assignment rates for the cSIMI and drSIMI approaches. The integrity rates are normalized to segmented objects in the raw images. Scale bar, 50 μm.