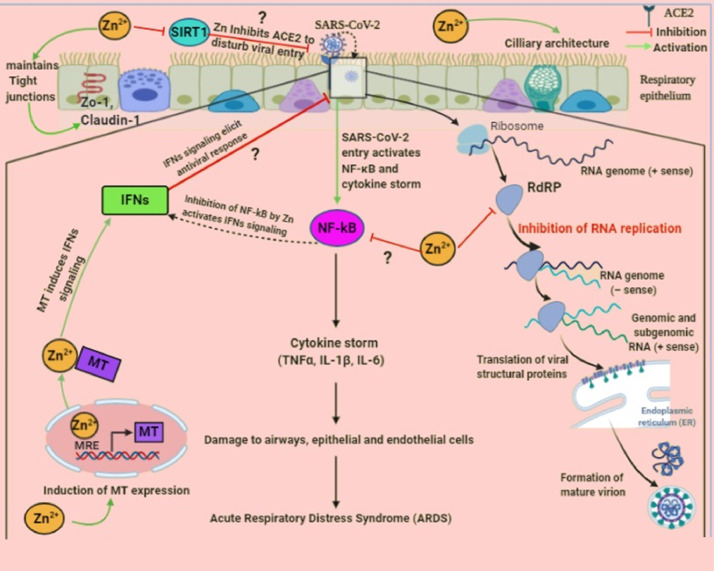
Fig. 3.
The underlying molecular mechanism of defense against SARS-CoV-2 infection by Zn in the respiratory epithelium. SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2 receptors on the respiratory epithelium and leads to activation of the inducible transcription factor, NF-κB. Subsequently, it induces the expression of various proinflammatory genes and results in the production of a “cytokine storm” which further damages airways cells and eventually provokes alveolar edema and ARDS. On the other hand, Zn may target multiple pathways to hamper the functional and structural consequences of inflammatory response caused by SARS-CoV-2.