Figure 1. Viral transfection and gamma-band resonance to stimulation.
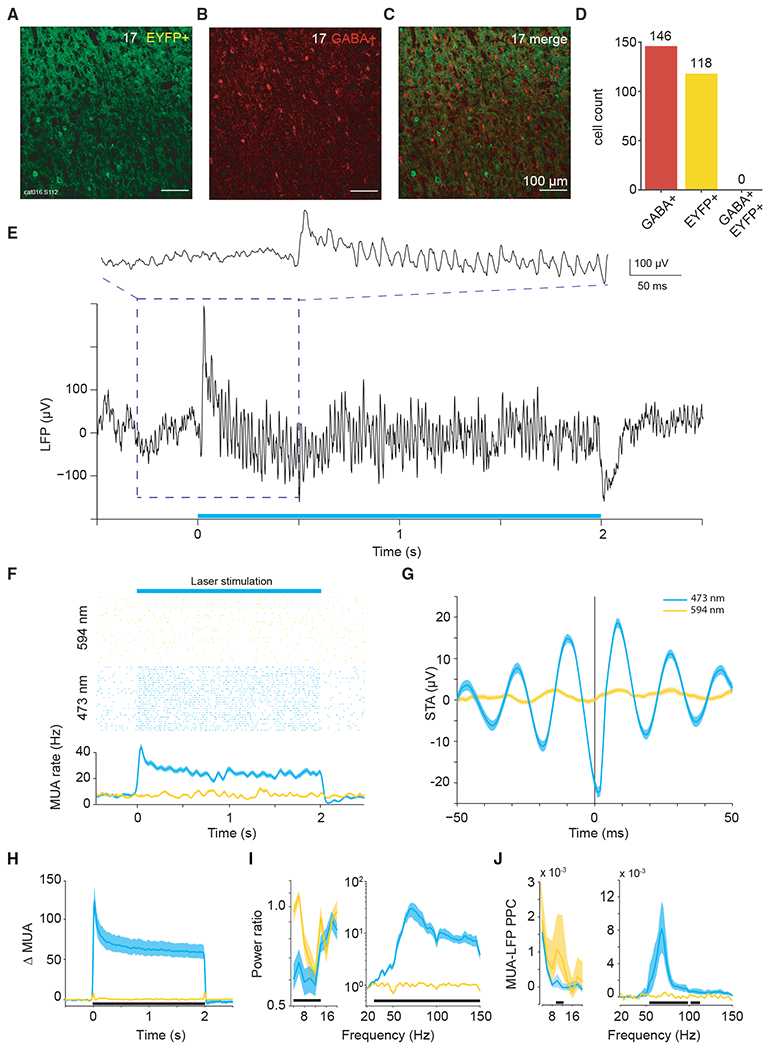
(A–C) Confocal microscopy images of immunohistochemistry performed on slices from area 17 after viral transfection.
(A) Endogenous fluorescence of ChR2-eYFP.
(B) Fluorescence from secondary antibody after staining for GABA+.
(C) Merged images, testing for neuronal co-labeling with ChR2-eYFP and GABA+ antibody. No co-labeled neurons can be found.
(D) Counts of GABA+-labeled neurons, EYFP+-labeled neurons, and co-labeled neurons in area 17.
(E) Example recording site in area 17 shows strong gamma-band activity in the local field potential induced by constant illumination.
(F) Robust MUA response to constant illumination at the same site.
(G) Spike-triggered LFP for example data shown in (E) and (F).
(H) Average MUA spike density change as a result of optogenetic stimulation. Smoothed by a Gaussian function (σ = 12.5 ms, truncated at ±2σ).
(I) Average LFP power ratio (optogenetic stimulation versus baseline) spectrum. Note different y axis scales for lower and higher frequency ranges.
(J) Average MUA-LFP PPC spectrum. Note different y axis scales for lower- and higher-frequency ranges.
(I and J) Use ±0.5-s epochs for the analyses from 4 to 20 Hz, and ±0.25-s-long epochs for the analyses from 20 to 150 Hz.
(F–J) Blue (yellow) lines show data obtained with 473 (594) nm light stimulation. Shaded area indicates ±1 SEM across trials. (H–J) Black bars at the bottom indicate frequency ranges with statistically significant (p < 0.05) differences between blue and yellow light stimulation, based on a cluster-level permutation test including correction for the multiple comparisons across frequencies.
