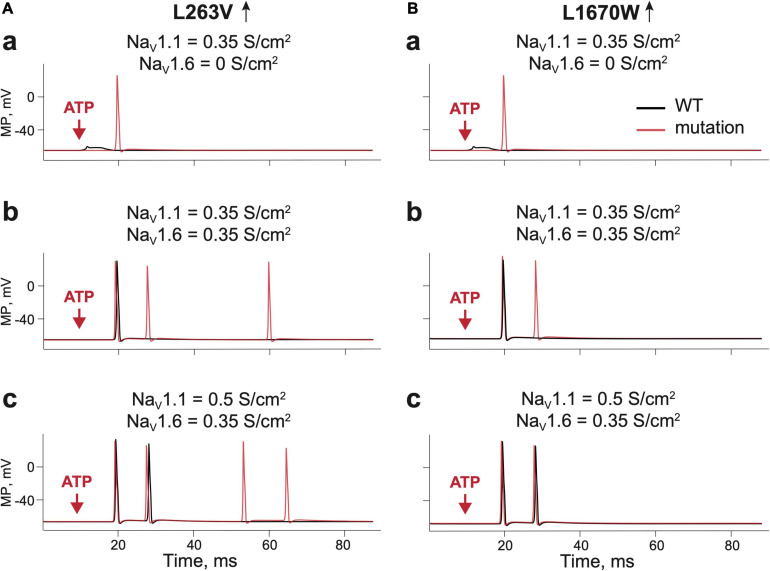
FIGURE 3.
Testing the role of NaV 1.1 and NaV1.6 in firing of Aδ-fiber with one branch and a single ATP release event. (Aa) The receptor potential in a single WT (Kahlig et al., 2008) fiber expressing NaV1.1 (black line) and firing in the fiber without NaV1.6. with L263V mutation (red line) of NaV1.1 with conductance 0.35 S/cm2. Of note, there is a membrane potential in the nerve compartment, where ATP is acting, whereas in other panels we present the appearance of the signal to the trigeminal ganglion. (Ab) WT (Kahlig et al., 2008) fiber (black line) and the L263V mutation (red line) with NaV1.1 and NaV1.6 (both with conductance 0.35 S/cm2) and; (Ac) WT (Kahlig et al., 2008) fiber (black line) and the L263V mutation (red line) with NaV1.1 conductance 0.5 S/cm2 and NaV1.6 conductance 0.35 S/cm2. (Ba) The receptor potential in a single WT (Dhifallah et al., 2018) fiber (black line) and L1670W mutation (red line) of NaV1.1 conductance 0.35 S/cm2 and without NaV1.6. (Bb) WT (Dhifallah et al., 2018) fiber (black line) and the L1670W mutation (red line) with NaV1.1 conductance 0.35 S/cm2 and NaV1.6 conductance 0.35 S/cm2. (Bc) WT (Dhifallah et al., 2018) fiber (black line) and the L1670W mutation (red line) with NaV1.1 conductance 0.5 S/cm2 and NaV1.6 conductance 0.35 S/cm2. ATP signaling is limited by partial hydrolysis.