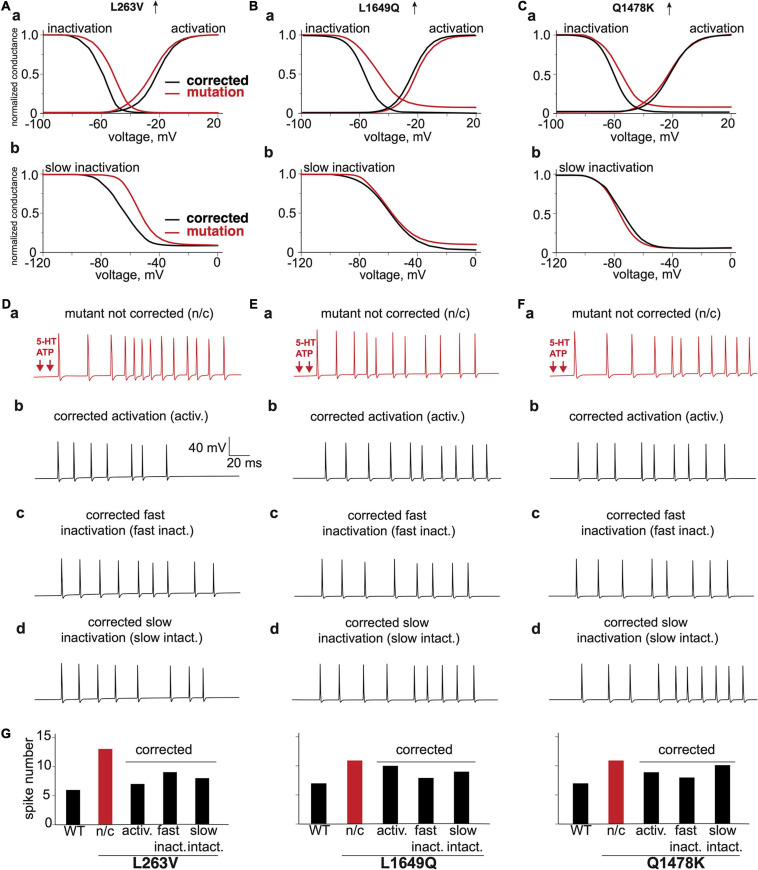
FIGURE 7.
The virtual correction of the abnormal phenotype via modification of voltage characteristics of mutated channels. The comparison of voltage dependence of corrected activation, fast inactivation and mutation (Aa) L263V, (Ba) L1649Q, (Ca) Q1478K. The comparison of voltage dependence of corrected slow inactivation and mutation (Ab) L263V, (Bb) L1649Q, and (Cb) Q1478K. (Da) L263V mutant fiber activated by ATP + 5-HT release events, (Db) with corrected activation, (Dc) with corrected fast inactivation, (Dd) with corrected slow inactivation. (Ea) L1649Q mutant fiber activated by ATP + 5-HT release events, (Eb) with corrected activation, (Ec) with corrected fast inactivation, (Ed) with corrected slow inactivation. (Fa) Q1478K mutant fiber activated by ATP + 5-HT release events, (Fb) with corrected activation, (Fc) with corrected fast inactivation, (Fd) with corrected slow inactivation. (G) The spike number of WT fiber and L263V, L1649Q, and Q1478K mutations with correction of activation and inactivation. ATP signaling is limited by partial hydrolysis and 5-HT signals are reduced by specific uptake.