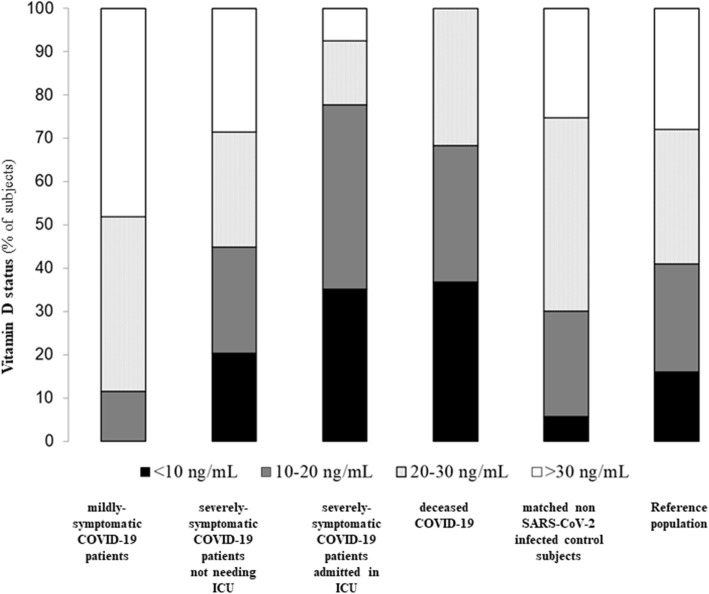
Fig. 3.
Prevalence rates of vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency and of severe hypovitaminosis D in mildly-symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infected subjects (mildly-symptomatic COVID-19), in COVID-19 patients admitted to hospital ward (COVID-19 non-ICU), in COVID-9 patients admitted to intensive care unit (COVID-19 ICU), in COVID-19 patients who died COVID-19 deceased) and in control subjects (matched controls). Legend: Data are shown as prevalence rates of vitamin D insufficiency (25OHD < 30 ng/mL), deficiency (25OHD < 20 ng/mL), or severe hypovitaminosis D (25OHD < 10 ng/mL) (B). ICU: intensive care Unit. Reference population: 3174 consecutive subjects, who underwent 25OHD measurement in Siena (Italy) between January 01 and March 31, 2020 in the frame of a routine health check with no epidemiological and clinical evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection