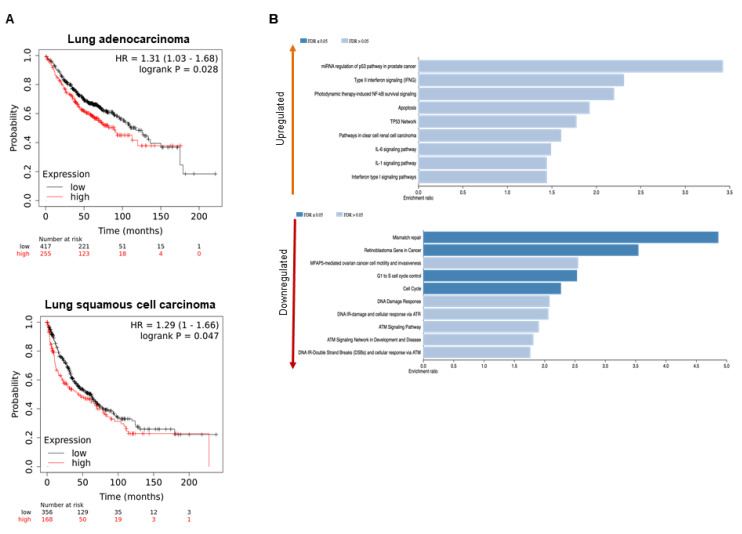
Figure 1.
Bioinformatics analyses to determine the prognostic value of PRMT5 and its major functional pathways in lung cancer (A) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of overall survival revealed that high PRMT5 expression was significantly associated with worse overall survival (OS) in both lung cancer subtypes of adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. (B) Using a publicly available dataset (GSE56757), the differentially expressed genes between PRMT5-silenced and control A549 lung cancer cells were identified and entered into WebGestalt tool to determine the top upregulated and downregulated functional pathways.