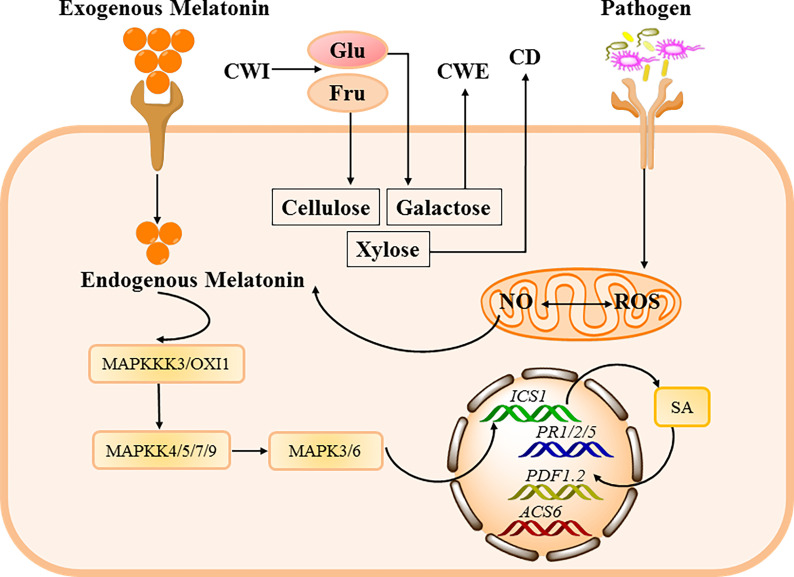
Figure 3.
The bacteriostatic mechanisms of melatonin in plants. Antibacterial mechanisms against plant pathogenic bacteria are characterized by up-regulation of defense genes such as plant defensin1.2 (PDF1.2), plant resistance 1/2/5 (PR1/2/5), and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase 6 (ACS6) through several signal transduction pathways, including augmentation of NO levels in plants, which collaborates with melatonin in up-regulating SA. Moreover, melatonin can stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) cascades, which in turn up-regulate SA biosynthesis gene isochorismate synthase 1 (ICS1). Additionally, high cell wall invertase (CWI) activity within melatonin-treated Arabidopsis leads to improved cell wall strengthening and callose-depositing factors (cellulose, xylose, and galactose).