Figure 3.
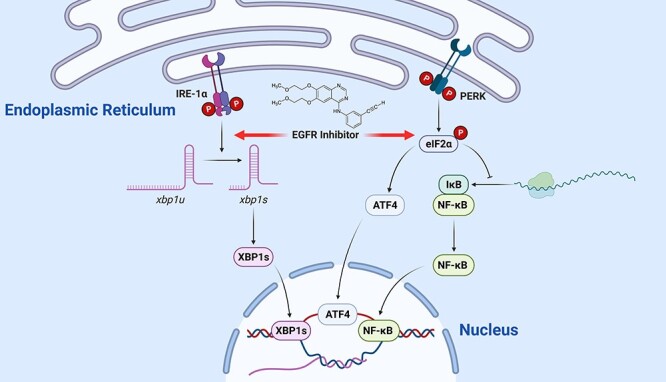
EGFR inhibitor causes inflammation in epithelium by triggering ER stress; following ER stress, PERK activates NF-κB via inhibiting IκB protein translation; this causes the release of NF-κB protein, which then carries out its role as transcription factor to promote inflammation; in addition, ER stress activates IRE-1α to initiate inflammatory response and apoptosis via splicing XBP1 mRNA; the spliced form of XBP1 (XBP1s) translocates into the nucleus and functions as transcription factor; EGFR inhibitors stimulate IRE-1α-mediated XBP1 slicing and PERK-mediated NF-κB activation; abbreviations: eIF2α, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; IκB protein, inhibitor of kappa B protein; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IRE-1α, serine/threonine-protein kinase/IRE1α; XBP1, X-box binding protein 1.
