Figure 4.
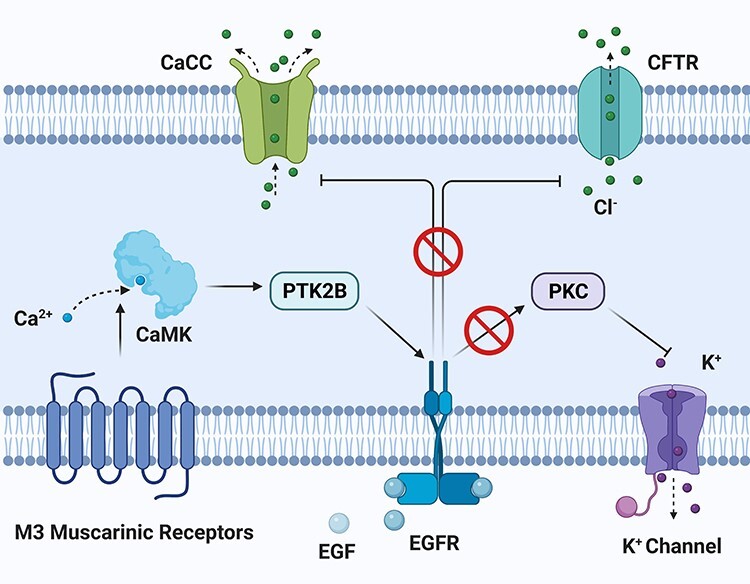
activation of EGFR suppresses Ca2+-dependent chloride secretion in epithelial cells; activation of M3 muscarinic receptor transactivates EGFR and eventually targets CaCC on apical side; the whole signal transduction involves CaMK and PTK2B; direct activation of EGFR by EGF inhibits chloride secretion on lumen side and simultaneously stimulates potassium channel on basal side; EGFR inhibitors are shown to block the inhibitory pathway from EGFR to chloride channel; abbreviations: CaMK, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; PTK2B, protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta; CaCC, Ca2+-activated chloride channel; CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; PKC, protein kinase C.
